July 2018 may be an important watershed for the US medical industry . Just two weeks ago, CMS (Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services) proposed a plan to formally incorporate telemedicine into the health care system. This means that formerly remote telemedicine may be officially stamped and certified as part of an effective and valuable medical process. After the change was passed, through telemedicine, more than 130 million American patients who were served by CMS will be able to access medical resources without geographical restrictions, and will be able to receive doctor's diagnosis faster than before. The concept of “telemedicine†has been proposed for decades and is not new. However, emerging technologies such as new materials, AI, big data, and AR/VR are giving it new meaning and broad market prospects. The number of telemedicine patients is also Climbing in the festival. Statistics and Forecasts of Global Telemedicine Patients 2013-2018 (Unit: Million) The proposal put forward by CMS is likely to start the first shot of the telemedicine industry's further outbreak: from medical entrepreneurial projects to large telemedicine companies, many players in this industry will have more clear commercialization. The path will also promote the continued expansion of this market, help break the current imbalance of medical resources and improve medical efficiency. Specific interpretation This program for the Physician Fee Schedule includes: "The doctor judges whether the patient needs further examination or treatment by remote means" and is included in the medical insurance payment system. Support high frequency road communication technology “The doctor evaluates the photos uploaded by the patients themselves†and is included in the medical insurance payment system. Expand Medicare-covered telemedicine services, which will include long-term preventive services It can be seen that the doctors and patients' attempts in telemedicine have been included in the past medical insurance payment system, and there is no longer any worries about the cost. It is possible to confirm whether the patient needs face-to-face diagnosis through remote consultation, and also reduce the doctor's burden. “CMS hopes to use emerging technologies such as audio and video applications and patient-side health platforms to help them easily access effective medical services. The redesigned family health service charging system encourages quality, not quantity, and removes those that may cause ' The cause of over-treatment," said CMS administration Seema Verma. This provision is of great significance for the real integration of telemedicine into the medical system. "The proposal of CMS has made many telemedicine related technologies have a broader market prospect in the future, and has also played a positive role in the standardization of the market." Silicon Valley medical-grade flexible wearables, telemedicine solution provider VivaLNK (Villing) ) Founder Dr. Li Jiang said. The company independently developed eskin electronic skin technology and background algorithms, which can make ultra-thin, soft and freely stretchable electronic patches fit closely with the human body, and monitor, collect and analyze various human bodies in real time and conveniently through the cloud platform. Signs parameters. "We have recently conducted in-depth cooperation with companies such as Alacrity Care and Myia on the remote diagnosis and treatment of cancer and cardiovascular diseases. It is expected that after the implementation of the CMS program, such cooperation will be more and smoother." In addition to the straightforward “buy-upâ€, CMS has also put forward a series of ideas, hoping to promote the sharing of electronic information between different medical institutions, improve the transparency of information in the overall medical industry, and effectively help doctors and medical institutions reduce the burden of affairs. Free up more experience and time to serve patients. For example, another idea in the PFS program: simplified, streamlined assessment and management required documentation; reduced unnecessary supervision of radiologists by non-essential doctors; and reduced over-complicated status reports for outpatients. According to CMS, after the implementation of this program, if a doctor has more than 40% of patients in the Medicare system, he/she can save 51 hours of work per year on average. Telemedicine trend The plan proposed by CMS this time is only one of its recent series of actions to improve medical efficiency. In March of this year, CMS launched the MyHealthEData program, which allows patients to have all of their health information, and can also send this information to any of their own medical service providers. Blue Button 2.0 means that patients can get all the past treatment and test information, and can also be provided to all other medical service providers. It is not difficult to see that as an important institution for managing medical insurance services, payment and information of more than 130 million patients in the United States, CMS is vigorously promoting the “removal of medical information barriers†and returning control over health information to patients. A major foundation for the further development of telemedicine. The largest player in telemedicine in the United States is Teladoc, a telemedicine company founded in 2013, and major medical insurance providers and large companies that provide remote diagnostics to patients with a market share of up to 75%. According to the 2017 data, it has served 17 million people, and the number of medical visits per year has increased from 120,000 in 2013 to nearly 1 million. After the adoption of this program by CMS, Teladoc is likely to welcome more partners. In addition to a large number of telemedicine providers like Teladoc, a range of related startups have more opportunities for commercialization. For example, AI+ medical robot Catalia Health. The company hopes to provide care management systems in different contexts through AI robots and algorithms. After the adoption of the CMS program, the medical assistant robotic solution used at home can be incorporated into the health care system, and future data may be linked to the medical system to provide more patient-related insights. The VivaLNK mentioned above is also an example. The company's Fever Scout body temperature products have been FDA-approved and listed in Australia, the United States and other countries and regions. Li Jiang told reporters that they also recently conducted a Developer Program to provide hardware products, algorithms and software-side assistance, including medical research institutions, sports companies, and related research departments of well-known universities. In Stanford, for example, in its collaboration with VivaLNK, VivaLNK's Vital Scout ECG products are used for data collection and 24-hour monitoring to study adolescent stress and Areas such as depression correlation. “Medical care is a field that covers many aspects and is very professional. Such a cooperation model allows professional companies and institutions to do professional things. For example, when doing Stanford research, if you can’t get continuous, different scenarios. Data, there may be no way to effectively measure important variables such as the degree of stress among adolescents," Li Jiang said. In the process of working with VivaLNK, Myia CEO Simon MacGibbon said, “Because VivaLNK's equipment output is complete and accurate, the team can fully meet the needs of customization, so that we can focus on exploring predictions, New ways to prevent and treat cardiovascular disease." With a clearer picture of the commercialization model, these players are likely to collaborate to create a new medical system: information belongs to patients, doctors are less burdened, medical services are more transparent, effective, and less geographically restricted. China's telemedicine market has broad prospects Although the policy of CMS can only affect patients in the United States, the US is the most active market and the largest economy in the world. Its policy orientation is a “barometer†for the global telemedicine market, and it is also useful for the Chinese market. In China, graded care has been implemented for several years, but the utility is still not obvious. The reason is that the electronicization of medical information in China has long been lagging behind. The information and systems between hospitals at all levels are scattered and fragmented, and there is no clear classification of medical services. Whether it is rehabilitation, outpatient or hospitalization, it is often mixed in a large In the hospital. This is gradually changing under the strong push of the government. At the beginning of 2015, the National Health and Family Planning Commission made it clear that online consultation is a strict medical practice. The main body of the service must be a medical institution, and the relevant policies for doctors to practice more. Since then, many doctors have been able to provide medical services in hospitals and online hospitals after submitting certificates such as medical qualification certificates and doctor's licenses. "From the current policy, more practice does not require the consent of the original unit. But I told the service unit that it has a good reputation on the Internet. Many patients will come here and promote each other online and offline, and will not affect offline work. Lin Zhizhen, deputy director of the Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Peking University First Hospital, said in an interview with the People’s Daily. According to data released by Xinhua News Agency, as of December 2017, China has achieved coverage of 13,000 medical institutions in telemedicine , and has carried out more than 60 million remote pathology, imaging, and cardiac diagnosis services. Due to technological advancement, medical image transmission is more convenient and rapid, and the expansion of network coverage also makes it easier for people to access online medical resources. Remote consultation has become an important part of the steps of supplementary review, consultation and post-operative follow-up in graded diagnosis and treatment. At the same time, the electronic medical record system of Chinese patients is gradually being established. Since 2010, after the establishment of the pilot office by the Hospital Management Research Institute of the Health Planning Commission, a series of electronic medical record related documents have been drafted, industry standards have been established, and the electronic evaluation of hospital medical records has been carried out. From the multiple dimensions of writing, coding, function, interconnection and management of electronic cases, the application is promoted. The recently released “Angelica†project of the OMAHA Alliance (OMAHA) is an attempt by industry stakeholders to promote the electronicization of medical information through blockchains. OMAHA is jointly established by well-known medical companies, government agencies, and media. It hopes to promote industry standardization, standardization and overall efficiency through collaboration. The white paper of the “Angelica†project reads: “I hope that everyone has a personal health record, so that ordinary people can get their own data, manage their own data, and use their own while ensuring privacy. Data, empowering data to individuals." From another perspective, the Chinese market has long been a problem of imbalanced medical resources, tilting towards coastal cities and first- and second-tier cities, and telemedicine can also help solve this problem. In April 2018, Premier Li Keqiang established three measures, "Internet + medical health" at the State Council executive meeting, hoping that "not only can improve the efficiency of medical services, make patients run less errands, it is more convenient, and more importantly, it can make More people share high-quality medical resources.†At the Huashan Hospital affiliated to Fudan University in Shanghai, his consultation center has completed more than 6,500 remote consultations covering more than 20 provinces and autonomous regions including Yunnan, Qinghai, Xinjiang and Tibet. “It can be seen that many provinces are now initiated by the government to establish telemedicine centers, trying to open up systems at all levels of townships, counties and cities, and thus narrowing the imbalance between medical infrastructure, medical environment and medical standards in urban and rural areas. The telemedicine market is gradually developing and the future prospects are very broad," said Lijiang, VivaLNK. Plastic Bucket Yellow Rice Wine Plastic Bucket Yellow Rice Wine is a type of rice wine that is fermented in a plastic bucket. It is a popular drink in many Asian countries, especially in China and Japan. The wine is made by fermenting glutinous rice with yeast and water, and then adding sugar to the mixture. The wine is then stored in a plastic bucket for several months until it is ready to be consumed. The yellow color of the wine comes from the rice used in the fermentation process. Plastic Bucket Yellow Rice Wine is typically served at room temperature and has a sweet, slightly tangy taste. It is often enjoyed with meals or as a social drink with friends and family. Barrel Packing Yellow Rice Alcohol,Cooking Liquor,Yellow Wine for Cooking,Bucket Packing Hua Diao Liquor Zhejiang Shengta Shaoxing Wine Co., Ltd. , https://www.shaoxingyellowricewine.com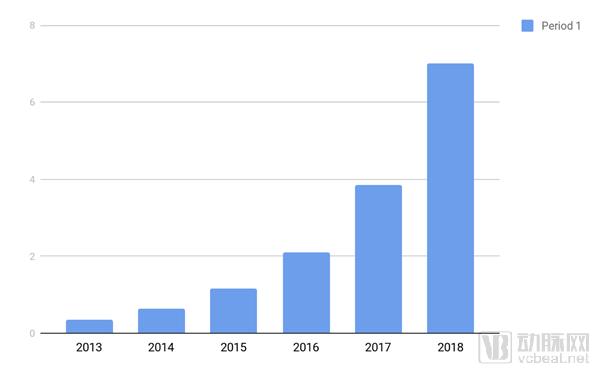
The US CMS proposes a new plan, and telemedicine faces major benefits.
