First, the election The transportation is convenient, there are cement roads, asphalt roads or higher roads nearby, and the distance from the sales area and storage area is appropriate. It facilitates the transportation of potato production materials and the successful shipment, sale and storage of harvested potatoes. In the terrain, you must choose a hillock (should have a slight slope, slope angle less than 5 degrees) or flat ground (drainage is relatively easy, and low waterlines are allowed inside). Pre-cropping crops: Avoid potatoes (heavy pods), sugar beet (poor, cold glutinous), Chinese cabbage (cold glutinous), and radish (cold glutinous rice). Corn cockles (flat cockroaches), wheat cockles (flat cockles), and soy cocoons (oil cockles) should be used. Second, the site preparation The cultivating machinery is used to deepen the boring and the depth is 35cm for the first pass and 40cm for the second pass. Third, prepare before sowing 1, germination Use amount: 150-180kg/mu, paved with outdoor brick or wooden floor, and covered with canvas or straw. Seedlings are ready 2 weeks before sowing. In the room, it can be used for germination, thickness is 3-4 layers, the temperature is maintained at 15-20 degrees, and the buds are 0.5-1.0cm long for 3-5 days. The seeds have germinated first, and germinated after uniform germination. Rebroadcast. 2, cut the block. It is generally recommended to use 40-60 grams of potato chips Fourth, sowing Sowing time: When the soil 15cm depth of ground temperature maintained above 7 °C and continued for 3 days to sow. Site preparation: The depth of the ditch is 12-15 cm. The sowing depth depends on the soil type: 8-12 cm, ie the height of the potato block from the ridge table. Sowing density: Seed potato: the number of sown plants was around 4500 plants/mu; commodity potato: the number of sown plants was around 3300 plants/mu. V. Farming management 1, cultivating soil links: when the young shoots top soil, one cultivator, shallow soil, after the seedlings are spawned, shovel the earthworms in time, raise the ground temperature with less soil, shovel the grass once again, pound two times, and cultivate more soil. The requirements for cultivating time: potato seedlings, budding period with potato top dressing for the third cultivator weeding. 2. Weeding: After cultivating, spray with Jintor + Seker. Spraying period: After weeding, weeds were sprayed with Seq + Sesquito before 2-3 leaf stage. 3. Fertilization: During the lifetime, the seedling stage requires less fertilizer, which accounts for about 25% of the total fertilizer requirement in the whole growth period. The tuber formation to the tuber growth stage requires the most fertilizer, accounting for more than 50% of the total fertilizer requirement in the whole growth period. , Starch accumulates and requires less fertilizer, which accounts for about 25% of the total fertilizer requirement for the whole growing period. Therefore, combining arable land with base fertilizers, the amount of nitrogen used accounts for about 80% of the total nutrients needed in the whole growth period, and all phosphorus and potassium are needed. Basal fertilizer should be dominated by farmyard fertilizers, and the application amount per mu should be 1-2t per pure manure. When basal deficiency is insufficient, it is concentrated into the sowing ditch. When the seedlings grow to 20cm, 25kg of ammonium bicarbonate is used per mu and 25kg of superphosphate is poured into the water. During the tuber expansion period, 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution was sprayed for 60 kg per mu and sprayed 2-3 times. 4. Water Management: Potato plants consume 708L of water per 1kg of dry matter, 1046-1228L of water in sandy soil, and 75% of potato roots have a depth of 45cm. Therefore, the depth of 45cm of soil water supply capacity can be used in the field. Moisture should be around 75%, especially in the field of tuber formation and expansion, the available water must maintain 70-80%. VI. Pest Control 1, late blight Take precautions. Use 70% Ansett WP 100 g/mu. 7-10 days spray once, even spray 5-7 times. 2. Early blight Take precautions. With 80% wettable powder 600 times. 7-10 days spray once, even spray 5-7 times. Medication rotation. 3, bacterial wilt Drought and crop rotation. Chemical control: At the beginning of the disease, pull out the plants, and irrigate the roots with 72% of agricultural streptomycin sulfate 4000 times. Fill each well with 250-500 g of liquid medicine. Irrigate once every 10 days for 2-3 times. . 4. Underground pest control Drought and crop rotation. Insecticide application of pesticide soil (with 1% dripping trichlorfon powder per acre 3-4 kg, adding fine soil 10 kg mixed dosing) liquid irrigation root (with 40% phoxim 1500- 2000 times liquid, irrigate root at seedling stage)
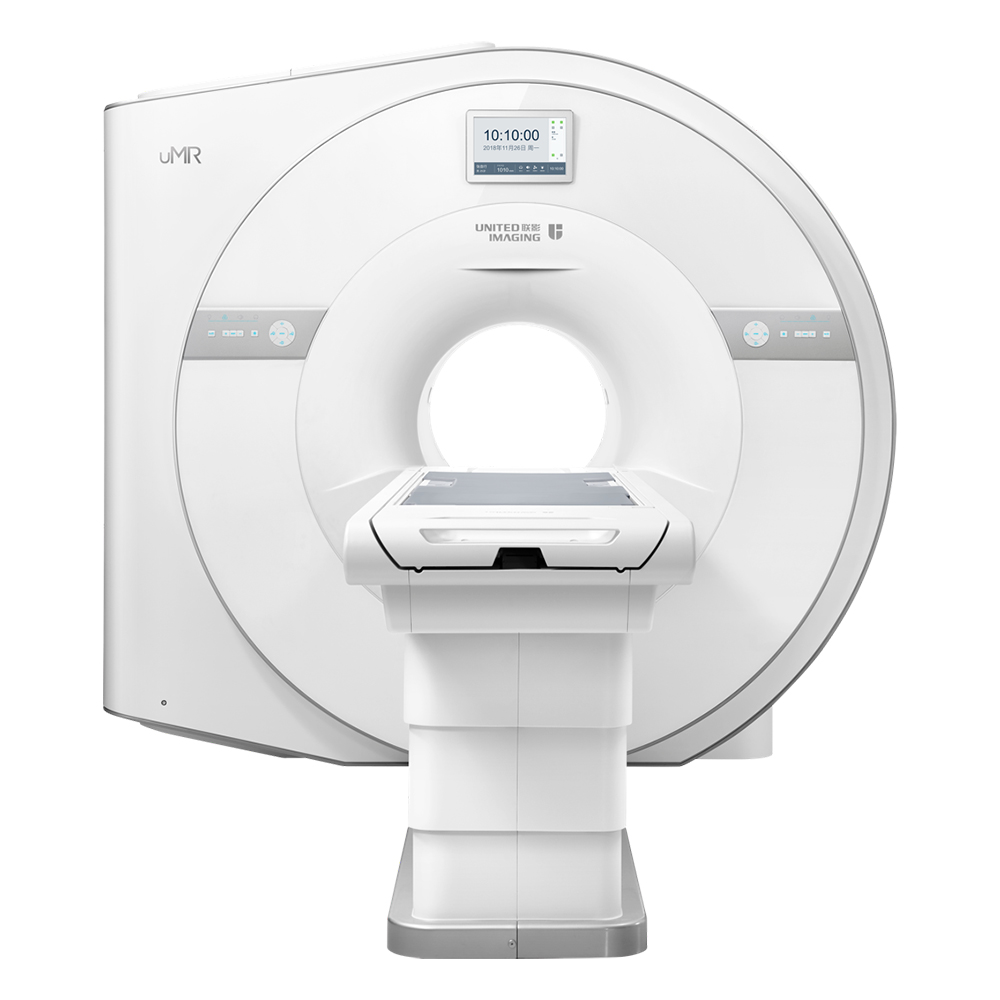
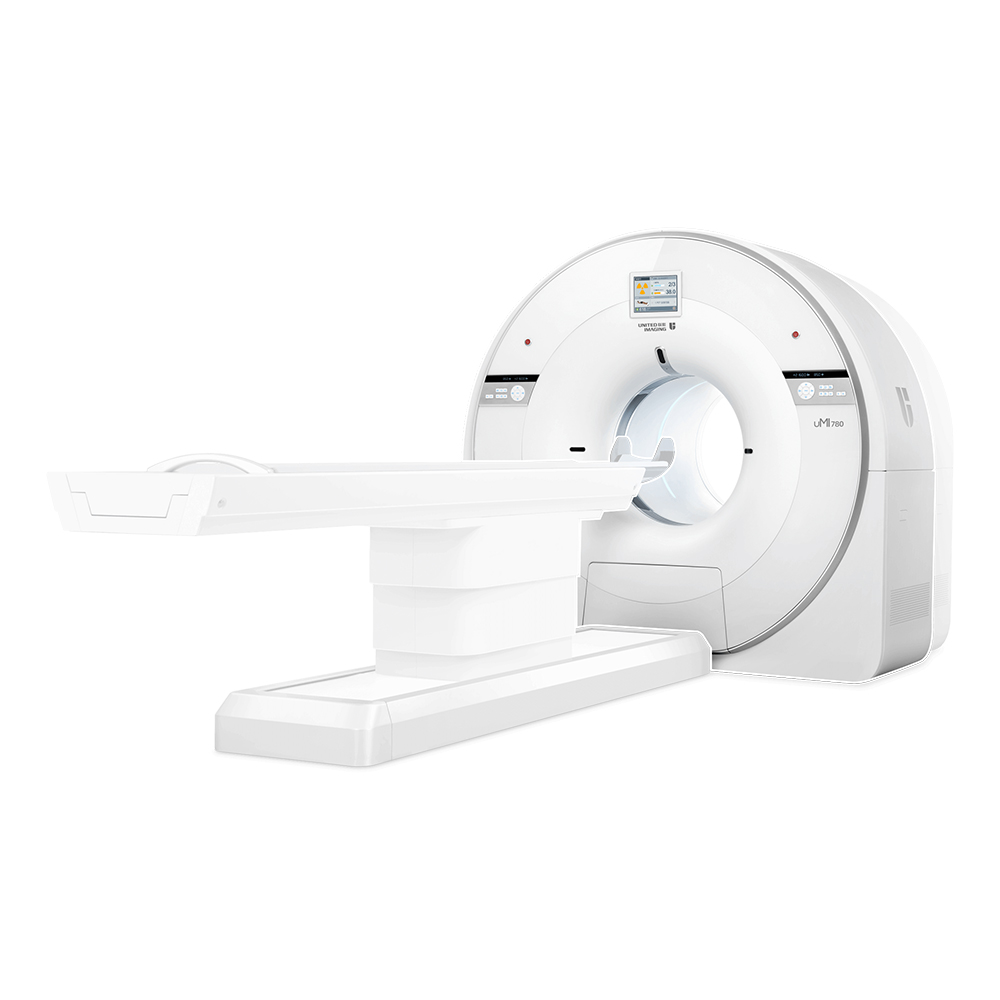
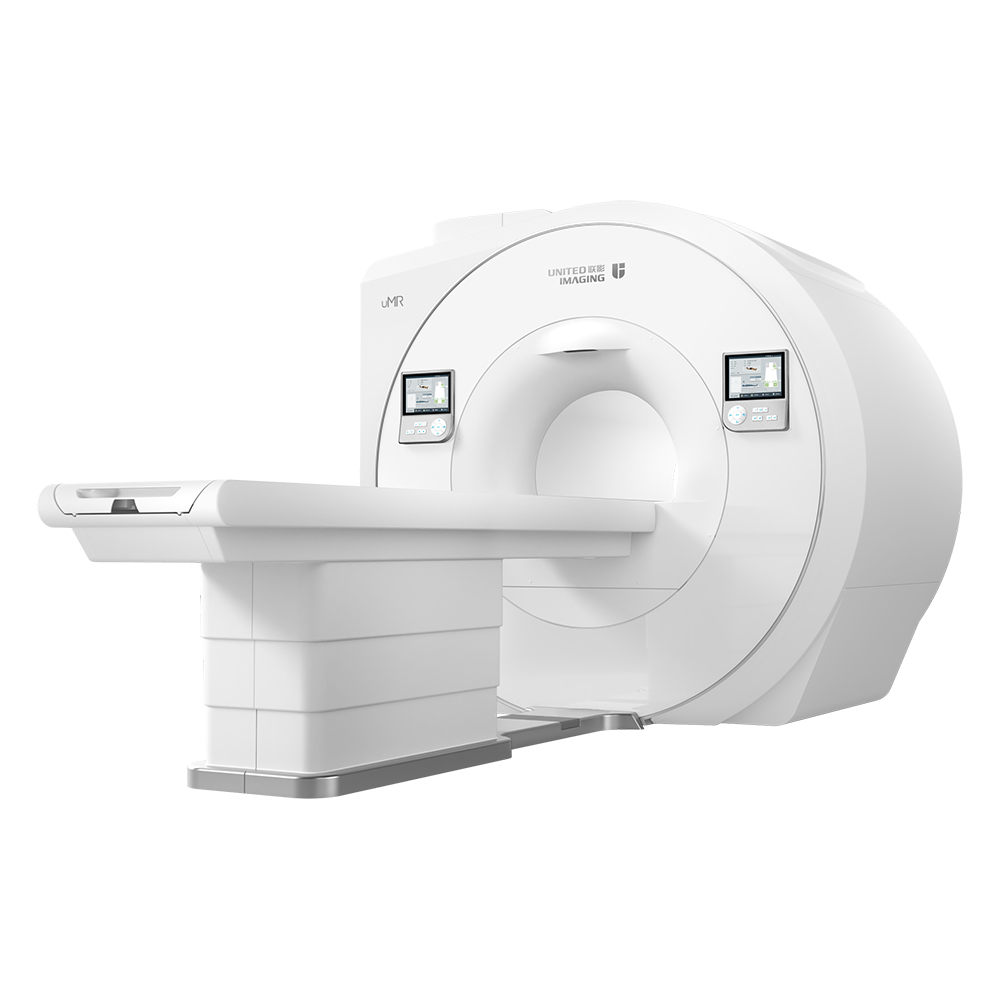
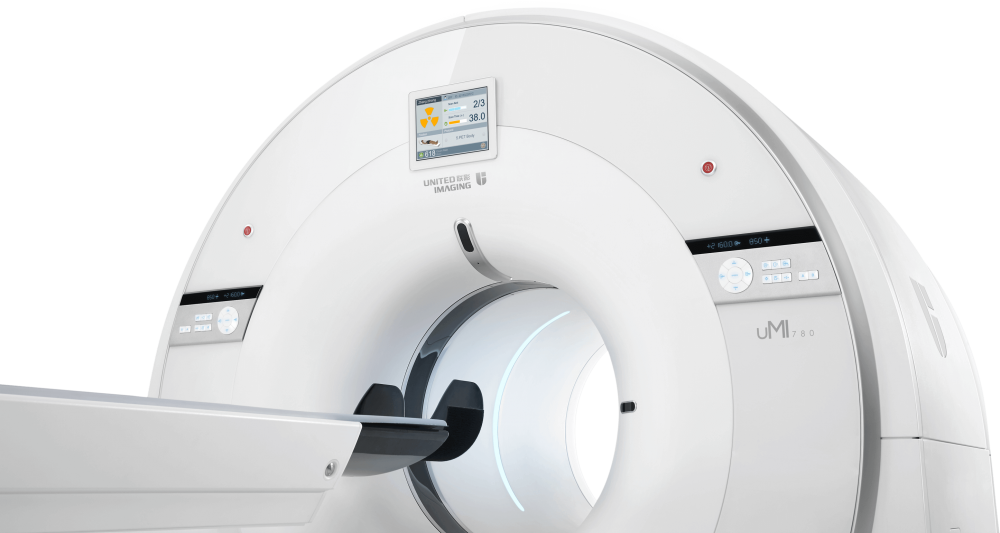
A CT scan makes use of computer-processed combinations of many X-ray images taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional (tomographic) images (virtual "slices") of specific areas of a scanned object, allowing the user to see inside the object without cutting.
Digital Radiography made affordable, Created to meet the needs of community to hospitals and private radiology practices, it enables the price-sensitive customers to join the drive to go digital.The versatile floor mounted radiography system enables you to go from film to CR to DR.Flooe-mounted easy for installation and operation
Computed Tomography,Medical Computed Tomography Scanning Machine,Medical Ct Scanner,Computed Tomography In Ct Scanner Shanghai Rocatti Biotechnology Co.,Ltd , https://www.ljdmedicals.com
The United-imaging is floor mounted system comprises a radiographic table with integral floor guide rail and a wallstabd. Requiring little room preparation, it is easy to install.
United-imaging according to the international advanced processing mode and standardlize design. the parts are made with precision CNC machine and moulding. Which adopt high degree of standardized, reasonable and compact structure. With reliable, durable and elegant appearance and advanced processing technology.
Efficient Cultivation Techniques of Winter Potatoes
