Background : Studies on stress in animals that have been sacrificed after anesthesia are common, but the effects of anesthesia on outcomes are under-researched. Our aim was to investigate the effects of different anesthetics, such as intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital or inhalation of isoflurane during acute stress response in rats. METHODS : Rats were randomly divided into electroshock (FS) and non-stressed controls. The procedure was further set up: direct decapitation, intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital or inhalation of isoflurane. A group of control group was injected intraperitoneally with normal saline and then killed by decapitation. Determination of plasma corticosterone (CORT), testosterone and estradiol, hypothalamic stress-related molecules expressed by corticotropin-releasing hormone, vasopressin and oxytocin, and NMDA receptor NR2B subunit expressed by frontal-related molecules , GABAA receptors and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. RESULTS : Direct decapitation and isoflurane shock (FS) significantly increased plasma corticosterone (CORT), whereas after intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium, this stress did not occur. Plasma corticosterone (CORT) was significantly increased in non-stressed control animals, either by injection of saline or sodium pentobarbital. The levels of sex hormones and the expression of related molecules mRNA in the brain were significantly different between the groups. CONCLUSIONS : Mixed injection anesthesia results in stress response in animals, impeding plasma corticosterone (CORT) levels, but affects plasma sex hormone levels and brain mRNA expression. Isoflurane inhalation stress response has less effect and is also optimal from the perspective of experimental animal ethics. figure 2
4%Echinacea Polyphenols Echinacea Purpurea Extract is a type of Echinacea Extract, which is our Key Product. It is a yellow-brown Powder Extracted, concentrated and dried from the stem and leaves of Echinacea.
health care for woman,Echinacea Purpurea Extract,Echinacea Purpurea Extract As,Echinacea Purpurea Angustifolia Extract,Echinacea Purpurea Root Extract Shaanxi Kepler Biotech Co.,Ltd , https://www.keplerherb.com
1 Introduction
The relationship between stress response and the etiology of affective disorder [1] promotes the study of stress response in animal models. The pressure regulation system is as follows: Thalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis activity has been under different stress activities. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) activity studies are driven by corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) mainly from the hypothalamus. Hypothalamus of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN). The ultimate goal of the HPA axis is the stress hormone hormone, which is mainly in rat corticosterone (CORT). We and other groups have found that sex hormones such as testosterone (T), estradiol (E2) and neuropeptides such as arginine vasopressin (AVP) and oxytocin (OXT) play important regulatory roles in the stress response [2].
The way in which animals are sacrificed to study possible confusion has caught our attention. Related Biological Studies There are two methods for killing animals: direct decapitation or anesthesia with a broken anesthesia. Decapitation may be a potential additional stress, depending on the investigator's experience and will affect the results [3]. Unconscious anesthetics seem to reduce the extra stress [4]. However, some drugs, such as phenobarbital, also cause additional stress, which is manifested by increased plasma CORT levels [5,6]. In addition, anesthetics affect excitatory receptors that inhibit brain activity, including the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor NR2B subunit and the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nnachr), through inhibitory receptors. Stimulation such as GABAA receptor (GABAAR) [7]. Whether to use anesthetics such as intraperitoneal injection (ip) sodium pentobarbital or isoflurane inhalation may affect the expression of brain mRNA in rats and the molecules involved in acute stress response, and it is not clear that intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital How to cause additional stress in animals.
Therefore, we analyzed the effects of experienced researchers on animals sacrificed in different ways. Rats were injected intraperitoneally with sodium pentobarbital and inhaled isoflurane (FS) and non-stimulated controls. The comparison included plasma CORT, T and E2 levels, hypothalamic CRH mRNA levels, AVP and OXT, and frontal lobe NMDA-NR2B, GABAAR, mRNA and nnAChR expression levels.
2. Experimental methods
2.1 Ethics Statement
All animal use and experiments were approved by the Chinese National Committee Zhejiang Branch in accordance with the Guidelines for the Use and Protection of Laboratory Animals (National Research Council, 1996, USA). Do your best to reduce animal suffering and use as few animals as possible (see Supplement 1 for more details).
2.2 electric shock rat
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (body weight 300-330 g) were housed in a room at 25-27 °C, alternating between 12 hours of light and dark, free to eat and drink. Give a week to adapt to the environment. A 0.5 mA electrical stimulation was proposed for 5 s, followed by an interval of 25 min. Animal living conditions and hygiene details together with FS protocol see auxiliary materials 1. Rats were randomly divided into 7 groups: 1) control or 2) FS by direct decapitation of rats (Huanglian Jiedu Decoction, FSD); 3) Control Or 4) FS rats were decapitated after 5 minutes of intraperitoneal injection of 3.5% sodium pentobarbital (3 ml/kg); 5) Control or 6) 4% isoflurane after oxygen inhalation 1– 2 minutes FS rats were killed by decapitation (Integrated Technology Research Institute or FSI group); 7) Additional control group was intraperitoneally injected with normal saline (3 ml/kg) for 5 minutes and then decapitated (CTR). 7 or 8 rats per group. Animals were sacrificed by the same investigator within 30 minutes of electric shock (FS) and the experiment was between 15:00-16:00 daily. Blood collection, centrifugation, and plasma collection. The rat brain, hypothalamus and frontal lobe were quickly removed for dissection. According to Paxinos and Watson's atlas [10], the hypothalamic anatomical location is 1.7 mm in the anterior temporal point.
All samples were immediately frozen and stored at −80 ° C until testing. All procedures are in accordance with the relevant regulations and laws of the local animal protection committee.
2.3 Determination of plasma hormone levels
Plasma CORT levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (RE52211, IBL Corporation, Germany). The internal and internal coefficients of variation of the variation (CV) were 3.38% and 10.50%, respectively. Plasma T levels were measured by radioimmunoassay (IM1087, Immunotech Corporation, USA) with an internal and inter-assay CV of 2.6% and 11.9%, respectively. Plasma E2 levels (ADI-900-174, Enzolifesciences Corporation, USA) were determined by an enzyme-linked immunoassay kit, one internal and across 3.9% and 11.37% CV, respectively.
2.4 Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) mRNA expression analysis in the hypothalamus and frontal lobe
The detection method of hypothalamic CRH, AVP mRNA and frontal NR2B, GABAAR and nnacr expression levels is photoconductive relay Q-PCR. In summary, all RNA was synthesized using Trizol extractant and gene and PrimeScript RT kit. Q-PCR was performed using a Bio-Rad cfx96 touch fluorescence PCR machine [11]. All procedures are performed in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Primer pair CRH, AVP, OXT, NR2B, GABAAR-receptor, nnacr and beta actin mRNA design and program Primer Premier 5. As a housekeeping gene (see Supplementary Material 2)
2.5 Statistics
Non-parametric tests are used when the data is found to be non-parametric. For multiple comparisons, the first – Wallis test used Kruskal, and if there were significant differences, the comparison between groups was further performed – Mann Whitney U test. P < 0.05 was considered important.
3. Results
3.1 plasma hormone levels
Plasma hormone levels were significantly higher in the FSD group (P < 0.001), but there was no significant difference between the T test (P = 0.834) or E2 levels (P = 0.248) compared with the CTRD group.
Similar results were observed when plasma FCT levels were significantly increased in the FSI group compared with the CTRI group (P < 0.001). There were no significant changes in plasma T (P = 1.000) and E2 Levels (P = 0.563). In contrast, the FSP group did not show significant changes in plasma CORT (P = 0.132), T (P = 0.848), or E2 levels (P = 0.949) compared with the CTRP group (Figure 1). In addition, the two CTRP (P = 0.008) and click-through rate (P = 0.004) groups were significantly higher than the plasma CORT level than the CTRD group, while the comprehensive technical study plasma CORT levels (P = 0.248) did not show significant differences compared with the CTRD group. (figure 1).
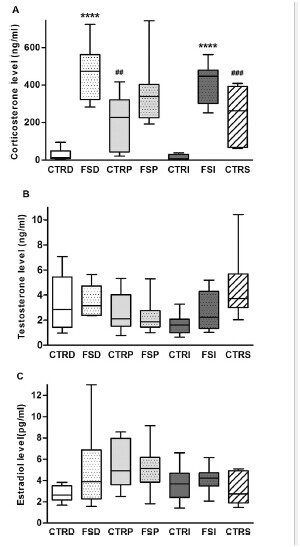
figure 1
3.2 Expression of related molecules in the hypothalamus and frontal lobe
Rats were sacrificed by electroshock FS stimulation. There was no significant difference in CRH, AVP mRNA expression in the hypothalamus and oxytocin or frontal NR2B, GABAAR, and nnacr (Fig. 2). 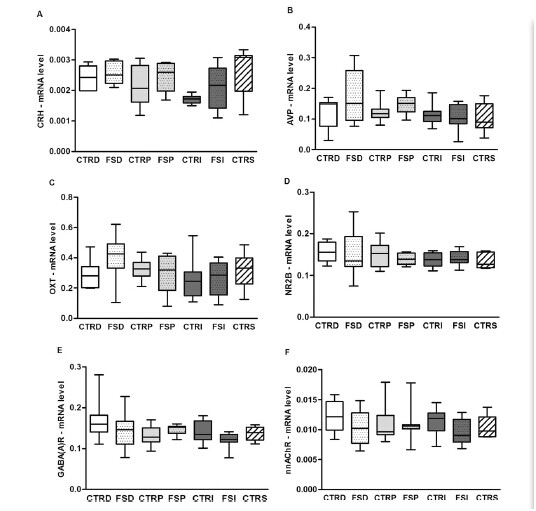
4. Discussion
Current studies have shown that intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital significantly increases basal plasma CORT levels, which may affect the results of the study. On the other hand, isoflurane inhalation anesthesia before decapitation did not affect basal plasma CORT levels. In fact, intraperitoneal injection of saline in the control group increased basal plasma CORT levels, indicating that additional stimulation was caused by intraperitoneal injection rather than pentobarbital. We also found that the use of anesthetics, ie intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital and inhalation of isoflurane, did not interfere with the measurement of brain stress-related mRNA molecules after 30 minutes of shock FS.
We found that rats who were directly decapitated after FS or killed by inhalation of isoflurane significantly increased plasma CORT levels, which is consistent with previous studies [12]. However, this stress response did not occur in the intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium injection group due to elevated cortisol levels in the non-FS group. A similar increase in plasma CORT was observed in the control group due to intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital and intraperitoneal injection of saline, while additional increases in plasma CORT levels did not occur in the isoflurane group or the direct decapitated control group, and the additional stress was clearly derived from The effect of the injection itself, rather than the sodium pentobarbital compound, confuses the results. It should be noted that after 20 min of FS electroporation male SD rats, we did not observe plasma T, E2 levels or hypothalamic CRH, AVP and oxtmrna levels or NR2B in the frontal cortex, nnachr GABAA receptor mRNA expression was significantly different. Expression of certain related molecules in certain regions may not respond until after 30 minutes or more of stress in male SD rats. The PVN CRH mRNA in the hypothalamus began to increase significantly, and the AVP mRNA at 2 h and 1 h began to increase the binding stress [13]. Although the OXT mRNA showed no change after 2 hours of fixation [14], it was significant after 4 hours of intraperitoneal injection of hypertonic saline. Increase [ 15 ]. These data can explain the stress-related changes in mRNA expression observed in our study. It should be noted, however, that the expression of some other molecular mRNAs, such as melanocortin receptor subtype 4 (MC4R) and proopiomelanocortin, indicates a significant increase in hypothalamus in male SD rats, from a similar within 30 minutes. FS shock stimulation began, and the expression of [16] CRH mRNA and MC4R mRNA in the amygdala increased significantly, indicating that FS induced changes in the molecular and brain regions.
Our data showed that after 30 minutes of electric shock, rats anesthetized before decapitation did not affect the plasma hormone levels or mRNA expression of hypothalamic and frontal lobe related molecules, but the implementation may affect plasma CORT levels, and the breakpoint of isoflurane seems to remain after inhalation. The integrity of the agonistic response is also the best choice for stress response studies from an ethical perspective.
Echinacea Purpurea,Native to some open woods and prairies of Manitoba and southeast Saskatchewan in Canada and south-central United States.Like light enough, warm climate conditions, suitable for the temperature of 15-28℃, strong, cold, drought resistance, the soil requirements are not strict, in the deep, fertile, rich in humus soil growth.
Echinacea is one of the great Herbs in Chinese medicine. It has a lot of good substances, so echinacea has a good immune stimulant effect. It can reduce the chance of inflammation in the body, and it can give the body an anti-bacterial and anti-viral effect.Can cause a large number of pathogenic cells to die or prevent their growth.
Echinacea is a great winter option for warding off the flu, it's good for some types of rheumatoid arthritis, it's also a great pain reliever, and it has no side effects.But while echinacea is a safe drug, it should not be taken for a long period of time. If you take echinacea for eight weeks, check with your doctor.If you often eat echinacea, you will feel your tongue will have a feeling of numbness, also will have a tingling sensation.This is normal.
Effects of sodium pentobarbital and isoflurane on acute stress response in rats
