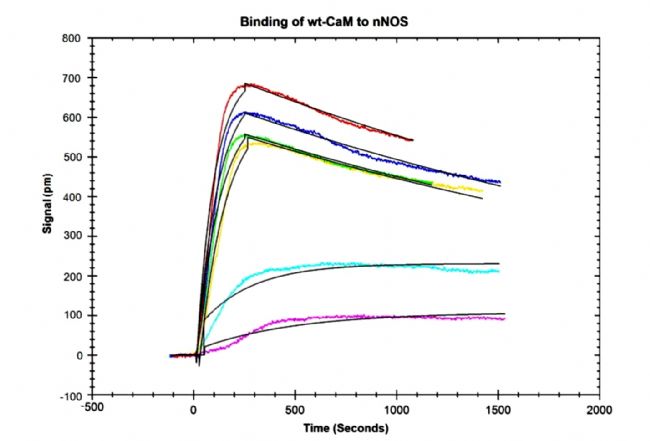
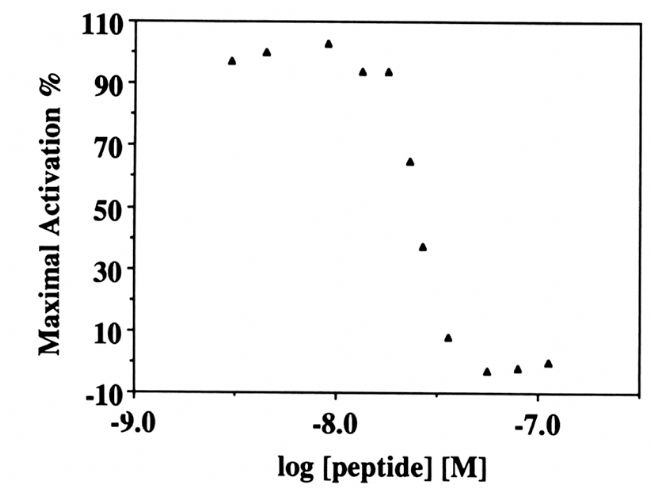
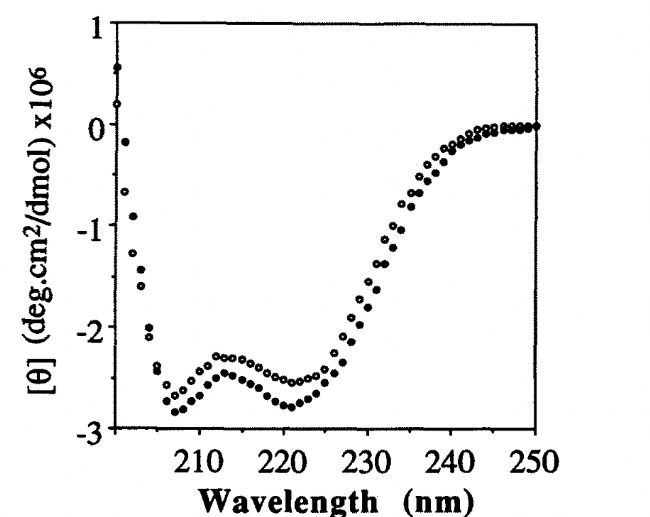
Typical application of new generation SPR innovation technology: Application of LSPR technology in detecting coupling kinetics of calmodulin and NO synthase targeting peptide Calmodulin (CaM) is a small molecule of acidic Ca 2+ -coupled protein that is involved in many physiological processes. Calmodulin can bind to many different proteins, thus affecting all aspects of cell function. Calmodulin is involved in the mediated process of life activity including inflammatory response, metabolism, apoptosis, muscle contraction, intracellular movement, short-term and long-term memory, nerve growth, and immune response. Some researchers have also found that calmodulin can function in the nucleus, which may be involved in the cleavage of pre-mRNA and regulation of ribosome aggregation and function. Many calmodulin-binding proteins do not bind calcium ions by themselves, and calcium ions act as important second messengers in the cell's signaling system, so these calmodulin-binding proteins can use CaM as a calcium sensor and signaling molecule. . CaM can adjust the orientation of its major regions and residue regions to accommodate its coupling with various targeting proteins and enzymes. The interaction of CaM with the targeting elements of these proteins requires activation of certain enzymes including NO synthase (NOS). ). Nicoya's personal molecular interaction instrument has been shown to be a well-established kinetic coupling constant for the interaction of CaM with NOS targeting peptides. To determine the binding, dissociation, and affinity constants of wild-type (WT) CaM and NOS peptide interactions, the researchers used the personal-type molecular interaction instrument to detect the coupling kinetics of the two before, and obtained the data and literature. The affinity constants obtained by the competitive coupling method were compared and analyzed. It was found that the matching results of the two methods were very consistent. ã€Detection method】: The NOS targeting peptide was immobilized on the chip, CaM was used as a flow analyte, and the CaM concentration was gradually decreased from the highest concentration. After multiple analyses, the TraceDrawer software was used to determine the binding rate, the dissociation rate and the affinity, using 1: 1 Coupling mode homogenization and fitting data. ã€result】: 1. The magnitude and binding slope of the CaM coupling curve decreases with the decrease of CaM concentration. With the decrease of CaM concentration, CaM binding, dissociation and surface regeneration are shown in Figure 1: Figure 1. Coupling of various concentrations of CaM on immobilized n-terminal peptide with SH-terminus 2. The dissociation rate obtained by the kinetic fitting of the CaM coupling data in Figure 1 is 3.34x10 -4 s -1 , and the binding rate is 1.56x105 M -1 s -1 . The obtained affinity constant (KD) is 2.20 nM Figure 2. Coupling kinetics analysis of the OpenSPR instrument between CaM and nNOS peptides: Analysis of the 1:1 coupling interaction pattern of TraceDrawer with a binding rate of 1.56x10 5 M -1 s -1 and a dissociation rate of 3.34x10 -4 "Characterization of the calmodulin-binding domain of rat cerebellar nitric oxide synthase," published in J Biol Chem, 2006. The interaction between calmodulin and NO synthase was tested by competition method. The ratio of enzyme interactions was titrated and the activity of PDE was affected by the competition of NO synthase with CaM for PDE. This result indicates that the site where PDE is coupled to NO synthase and the site where PDE is coupled to the main region of CaM Consistently, the experimental results confirmed that the affinity constant of the peptide was 2.2 nm. Figure 3. CaM-dependent periodic nucleic acid phosphate. Figure 4. CNOS in a pH 5.0 aqueous solution. A series of partitioned enzymes are inhibited by cNOS peptide. Figure 5. Titration of cNOS peptide with TEF in 5 mM citric acid solution. Figure 6. Absorption spectra of Ca 2+ -CaM and CaM-cNOS peptide complexes. The Nicoya Personal Molecular Interaction Analyzer uses a new generation of LSPR-free detection technology with a CaM-cNOS affinity constant of 2.2 nM and CaM-cNOS affinity obtained by competitive analysis published on J Biol Chem in 2006. The constant 2.2nM is completely consistent, which perfectly verifies the feasibility and reliability of the application of Nicoya label-free innovative detection technology in the study of CaM-cNOS coupling kinetics. Waist massager Waist massager Shenzhen Jie Zhong Lian Investment Co., Ltd. , https://www.szmeizon.com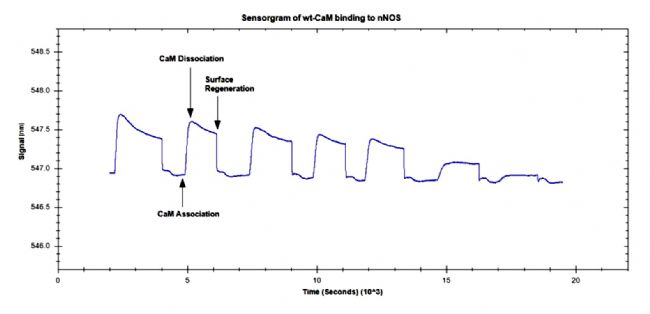
Nicoya Personal Analyzer Advantages:
Typical application of new generation SPR innovation technology: application of LSPR technology in detecting coupling kinetics of calmodulin and NO synthetase targeting peptide
