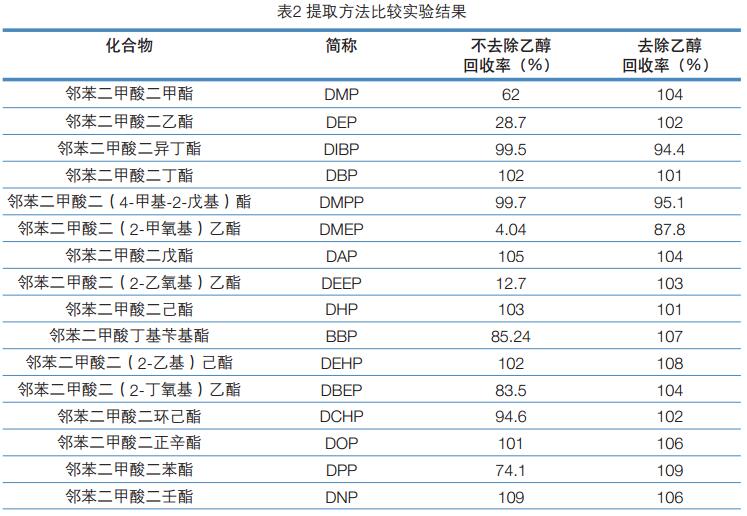
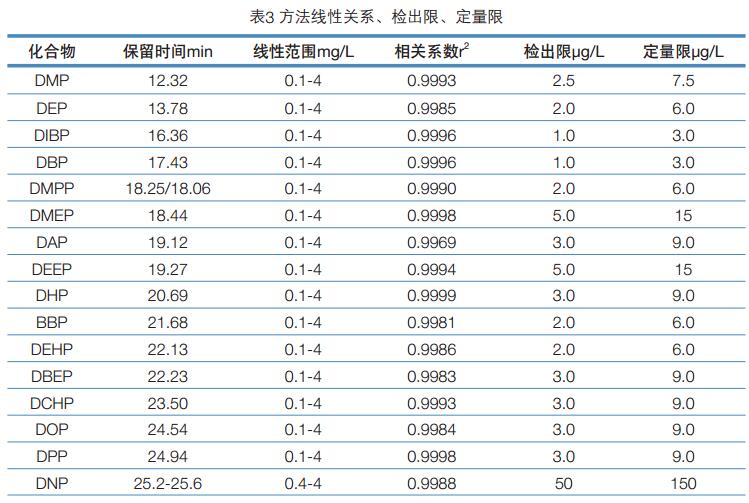
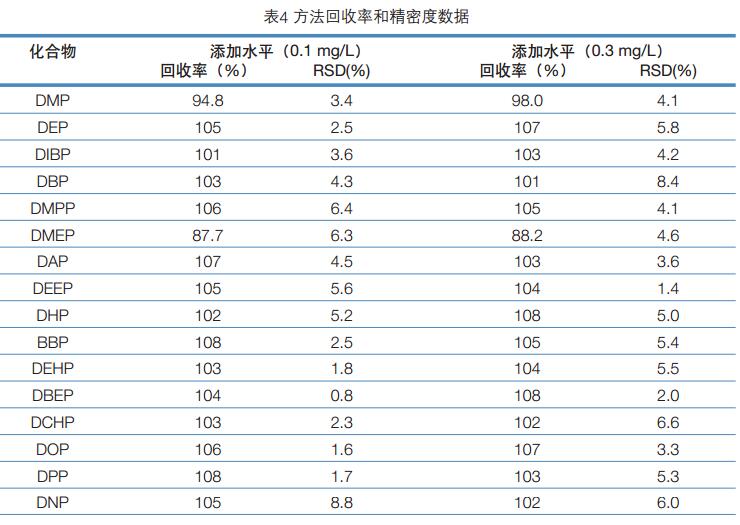
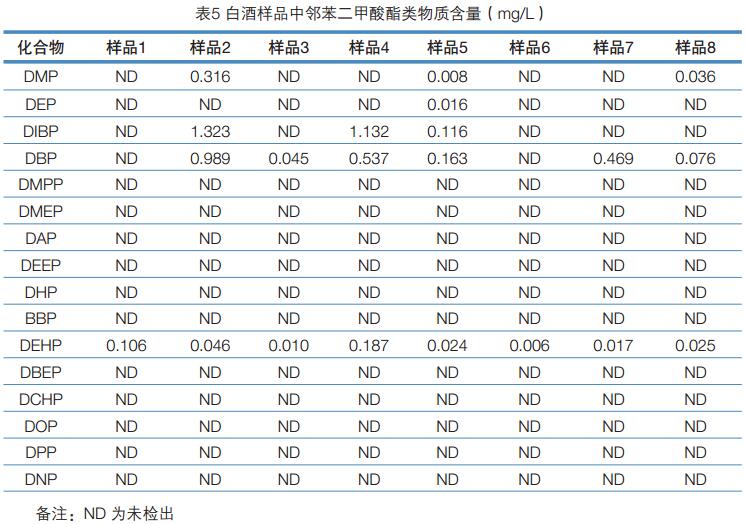
Key words: GC-FID; liquor; phthalate Summary A gas chromatographic method for the determination of 16 phthalate esters in liquor was established. The sample was removed from ethanol and extracted with n-hexane and detected by GC-FID. In the range of 0.10 to 4.0 mg/L, the linear relationship between the peak area of ​​the target and its mass concentration is good (R 2 >0.99). At the addition level of 0.10 and 0.30 mg/L, the average recovery of sample addition was 87.7-108%, and the relative standard deviation (RSD, n=5) was 0.8-8.8%. The method detection limit was 50 μg/L except for dinonyl phthalate. The other 15 compounds were 1.0-5.0 μg/L, and the limit of quantification was 3.0-15 μg/L. The method has the advantages of sensitivity, simplicity, rapidity, accuracy, wide linear range, and the like, and can meet the detection requirements of phthalate esters in liquor. introduction Phthalate Acid Esters (PAEs, also known as phthalates), commonly used as plasticizers and softeners in the plastics industry, are used to increase plasticity and plasticity. Resilience and increase the strength of plastics. PAEs are environmental hormones that mimic the natural hormones in the body, interfere with the effects of normal hormones, affect the most basic physiological regulation functions in the body, have carcinogenic, teratogenic and mutagenic effects, and pose a hazard to human health. On June 1, 2011, the Ministry of Health issued a notice stating that phthalate esters were clearly classified as non-edible substances added to the ban and were prohibited from being used in food. PAEs mainly enter food through food packaging materials, and ethanol in liquor has good solubility for PAEs, so there is also a risk of contamination of such compounds in liquor. On November 19, 2012, some media reported that according to third-party testing, the plasticizer content in a famous domestic brand of liquor exceeded 260%, and there was an unexpected fatal danger. At present, GB/T 21911-2008 "Determination of phthalates in foods" has been promulgated in China. According to this standard, the experiment was optimized. After removing ethanol, the extraction of n-hexane and gas chromatography showed that the detection method of phthalate residues in liquor was established. The method has the advantages of sensitivity, rapidity, accuracy, wide linear range, and the like, and can meet the detection requirements of phthalate esters in liquor. Experimental part Main equipment and reagents Instrument: Trace 1310 Gas Chromatograph (ThermoFisher) with FID detector. Sample preparation method Accurately measure 5.0 mL of white wine sample in a 10 mL stoppered glass centrifuge tube, heat to remove ethanol in the sample in a boiling water bath, cool to room temperature, add 2.0 mL of n-hexane, shake and extract, and place the supernatant after standing. Sample determination Instrument conditions are shown in Table 1. Results and discussion Selection of sample extraction conditions Liquor contains 30 to 60% vol of ethanol. Since ethanol has a good solubility to phthalate compounds, it is less effective when extracting phthalate compounds in liquor using a n-hexane solvent. The error caused by ethanol can be avoided by first removing the ethanol from the wine and then using the hexane extraction analysis. Accurately measure 5.0 mL of white wine sample, the addition level is 0.80 mg/L, and it is 3 times in parallel. The extraction method of sample extraction and recovery is carried out by using two methods of removing ethanol and not removing ethanol. The results of the addition and recovery experiments are shown in Table 2. The experimental results show that the sample recovery and recovery experiment using the ethanol extraction method has a good recovery rate. Method linearity, detection limit and limit of quantitation A series of mixed standard solutions with concentrations of 0.10, 0.20, 0.40, 0.80, 1.00, 2.00, and 4.00 mg/L were prepared, and the samples were sequentially injected from a low concentration to a high concentration, and linear regression was performed with a mass concentration and a peak area as a standard curve. The results showed that there were 15 linear phthalate esters in the range of 0.10~4.00 mg/L. The DNP response is poor and the linear range is 0.40 to 4.00 mg/L. Using the method of adding the target compound to the sample, the detection limit is calculated according to the characteristic ion mass chromatographic peak signal-to-noise ratio R S/N = 3, and the quantitative limit of R S/N = 10 is calculated. The results are shown in Table 3. Determination of method precision and recovery The liquor samples were weighed and two standard samples of horizontal concentration were added, and each concentration level was measured in parallel five times. The results showed that the average recovery was 87.7-108%, and the relative standard deviation (RSD, n=5) was 0.8-8.8%. The recovery and precision data results are shown in Table 4. Determination of phthalate esters in 8 liquor samples The residual amount of phthalate esters in the eight commercially available liquor samples was measured by the above pretreatment method, and the measurement results are shown in Table 5. The results of sample determination showed that DIBP, DBP and DEHP were common in liquor, and the content of DIBP and DBP was higher. GB9685-2008 "Sanitary Standards for the Use of Additives in Food Containers and Packaging Materials" stipulates that the maximum residues of DEHP, DINP and DBP are 1.5 mg/Kg, 9.0 mg/Kg and 0.3 mg/Kg, respectively. The content of DBP in the three samples exceeded the regulation, and the highest sample had a DBP content of 0.989 mg/L, which exceeded the standard by 230%. The standard and sample addition spectra are shown in Figure 1. in conclusion The method adopts the technique of removing hexane from ethanol and extracting by gas chromatography to establish an analytical method for 16 phthalate residues in liquor. At the two addition levels of 0.1 and 0.3 mg/L, the recovery was 87.7-108%, and the relative standard deviation (RSD, n=5) was 0.8-8.8%. The method detection limit was divided by didecyl phthalate. Outside of 50 μg/L, the remaining 15 compounds ranged from 1.0 to 5.0 μg/L with a limit of quantitation of 3.0 to 15 μg/L. The method has the advantages of sensitivity, simplicity, rapidity, accuracy, wide linear range, and the like, and can meet the detection requirements of phthalate esters in liquor. Ring Video Doorbell,Home Security Doorbell Camera,Security Doorbell Camera,Ring Doorbell Camera Shenzhen Zuomi Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.zuomicamera.com
Key words: GC-FID; distilled spirit; PAEs
Reagents: n-hexane, chromatographically pure (ThermoFisher); 16 phthalate standard mixed solutions (O2Si, USA).
Samples: 8 brands of liquor, purchased in supermarkets. 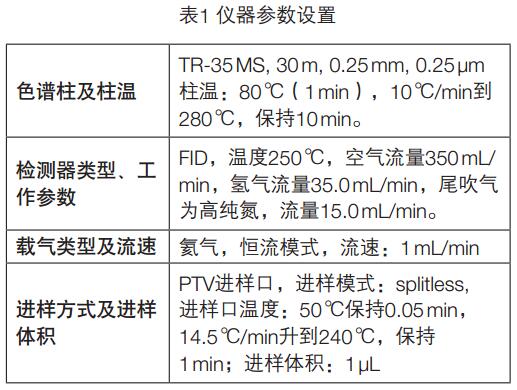
Determination of Phthalate Residues in Liquor by GC Method
