1 experimental part 3 conclusions
Penicillin can produce penicillin thiazoic acid by penicillinase, and the reaction process is as follows: 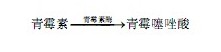
The acid can be ionized to produce H, which is a strong acid, so the rate at which the enzyme catalyzes the reaction can be expressed by the change in acidity, according to the kinetic equation of the Micari-Mendon reaction: ![]()
The rate of the catalytic reaction is related to the enzyme and the substrate. When the concentration [S] of the substrate is large, the reaction rate is independent of [S], and is only proportional to the total concentration of the enzyme, so that it can be determined by the change of acidity. The concentration of the enzyme. In order to find the best test conditions, we chose the enzyme to catalyze the appropriate temperature, and the substrate concentration is affected by the buffer capacity. Among them, the blank is PBS without enzyme, so that some other interference factors in the experiment can be deducted, and different concentrations of penicillinase solution can be configured with PBS as solvent, and the qualitative test is done before, and then the milk solution is prepared with skim milk powder. After equivalent pasteurization, do penicillin decomposition experiments. (The following data are deducted from the blank).
2 Results analysis and discussion
2.1 Select buffer capacity
Here, a certain amount of buffer solution is selected to simulate, considering that the milk itself has a certain buffering capacity. Finally, 0.025 mol/L, pH 7.0 PBS solution was selected.
2.2 Optimal temperature selection
Compare the effects of different temperatures on the enzyme activity, and finally choose the optimum temperature of 25 °C to carry out the next experimental work.
2.3 The storage of the substrate is selected
A penicillin solution having a size of 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 mg/ml was prepared in PBS, and 50 IU/ml of penicillinase was separately added, and after 30 minutes of reaction, a change curve was obtained.
According to the Micari-Mendon principle, when the substrate concentration is sufficiently large, the rate of catalysis of the enzyme is independent of the substrate concentration. It can be seen that with the increase of the concentration of penicillin substrate, when the concentration of penicillinase is constant, the corresponding enzyme-catalyzed reaction rate also increases, and when the concentration of penicillin reaches 20 mg/ml, the reaction rate is basically reached. Maximum value. In order to obtain a stabilizing effect, the concentration of the penicillin substrate was finally selected to be 25 mg/m1.
2.4 Determination of the working curve
It can be seen that penicillinase is added to the penicillin solution prepared in PBS, and the pH value decreases with time. Figure 1 is obtained from pH = pH 30 min - pH 0 min. It can be seen from Figure 1 that for the rate of enzyme catalysis, proportional to the total concentration of the enzyme, the reaction rate of penicillin decomposition is increased when the penicillinase concentration is increased. It is linear between 10-5050 IU/ml. With the increase in penicillinase concentration, the minimum detection limit is 10 IU/ml. 
From the penicillin solution prepared with milk, the pH of the reaction process of adding different concentrations of penicillin can be seen that for the case of solvent milk, the similar changes of PBS are also presented: as long as the concentration of penicillin is increased, penicillin The rate of decomposition of the decomposition is accelerated, wherein ?pH = pH 30 min - pH 0 min. Figure 2 shows the pH value of the milk solution under the action of penicillinase at different concentrations. It can be seen from the figure that when the penicillinase concentration is continuously increased, the same increase in pH is also inevitable, which also presents a certain Linear relationship, where 8 IU/ml is the minimum detection limit. 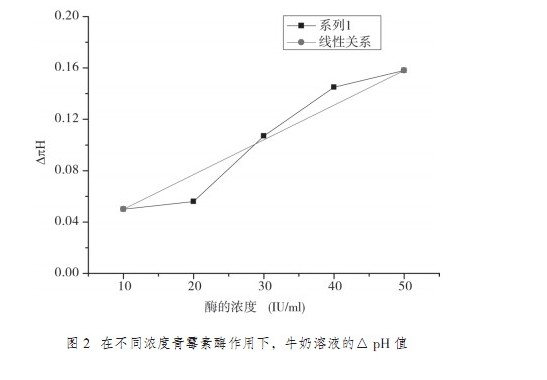
When the concentration of the substrate is large, the reaction rate is independent of the substrate. In this experiment, penicillin at a concentration of 25 mg/ml is used as a substrate. When the concentration of penicillinase increases, the rate of decomposition of penicillin increases, and the pH changes. In the detection of standard milk samples, the minimum detection limit is 8 IU/ml. The next step is to increase the density of the points and draw a test curve for the actual milk sample detection.
Application of acidity meter in detecting residual penicillinase in milk
