m6A RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing m5C RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing m1A RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing Ultra-micro m6A methylation sequencing Colorimetric detection of overall methylation levels Whole transcriptome sequencing ChIP sequencing RIP sequencing Nat. commun|Mettl3-mediated m6A RNA methylation regulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteoporosis Nature|m6A RNA methylation recognition protein YTHDF1 is involved in memory formation No, Da Niu tells you how to study lncRNA methylation RNA methylation enters the ultra-micro era More than 10 points of m6A RNA methylation sequencing article----Cloud order bio-assisting RNA methylation in 20 points, coexistence of heat and strength Cloud Sequence Bio's latest m6A "RNA methylation" research summary - non-coding RNA articles Cloud Sequence Bio's Latest "RNA Methylation" Research Summary - Arabidopsis Cloud Sequence Bio's latest m6A "RNA methylation" research summary - virus articles Plant Cell: Arabidopsis found a new m6A RNA demethylation modifying enzyme Cloud order customer 12 points top article, teach you how to use RIP sequencing to play the molecular mechanism! 2018 Nature Magazine's Breakthrough Research Results--m5C RNA Methylation Cloud Sequence Creature Nature Breakthrough Research - RNA Methylation Newly Modified m1A Cloud Sequence Creature Nature Heavy: m6A RNA methylation is involved in the key aspects of hematopoietic stem cell development! Cancer Cell: Professor He Chuan discovers important functions of m6A RNA methylation Xiaobai must see! Summary of methods for identification of overall level of RNA methylation Hepatology: m6A RNA methylase METTL3 promotes the development of liver cancer Yunxu Bio exclusive m5C RNA methylation sequencing Nature article reveals multiple functions of RNA methylation Filling the gap of epigenetic modification: a new mechanism for RNA methylation regulation gene export ENT Pack,Disposable ENT Pack,Disposable ENT Operation Pack,Disposable Eye ENT Drape Pack Xinxiang Huaxi Sanitary Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.huaximedical.com
As a pluripotent cell, embryonic stem cells produce cells of all tissues and organs of an animal by proliferating and differentiating. Studies have shown that m6A RNA methylation in embryonic stem cells is mostly related to cell proliferation [1-2] and immune response [4]. However, there is no relevant report on the molecular mechanism of m6A modification in the differentiation of embryonic stem cells into neuroendodermal cells. Today, I shared a research team from the University of Cambridge in England published in Nature in August 2018 (Influencing Factor: 40.14) to talk about the mechanism of RNA methylation in regulating embryonic stem cell differentiation. The beginning of this article is very straightforward. First, the gene of interest SMAD2/3 was identified by reading the literature. After co-IP and mass spectrometry, it showed that it can directly interact with methyltransferases METTL3, METTL14 and WTAP. . They are stars, and the molecules they bind are also star molecules. No, researchers in embryonic stem cells have found that SMAD2/3 binds to METTL3 and METTL14. As expected, this combination plays an important role in embryonic stem cells. . 
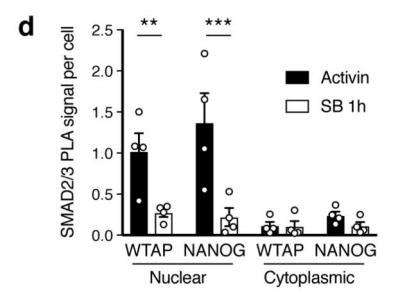
1.SMAD2 / 3 protein METTL3-METTL14-WTAP OF <br> first binding complex by in vitro stimulation, inducing human embryonic stem cells into neural ectodermal cells, and to provide this technology by Co-IP tandem mass spectrometry (cloud Biological Sequence Experimental) technique to compare proteins that bind directly to the SMAD2/3 antibody in both cells. The results showed that a total of 89 proteins were found. After the intersection, 78 consensus proteins were obtained and mapped into a network map. These proteins were found to be involved in the TGF-β signaling pathway and the biological process of mRNA. The methylation transferase--METTL3-METTL14-WTAP complex in the radicalization interacts directly. This result is consistent with the post-WB validation and inhibition of the SM-D2/3 phosphorylation site after Co-IP results. PLA experiments confirmed that the binding between the two mainly occurred in the nucleus, and after being stimulated by Activin, it affected the expression of nuclear transcription factor NANOG. 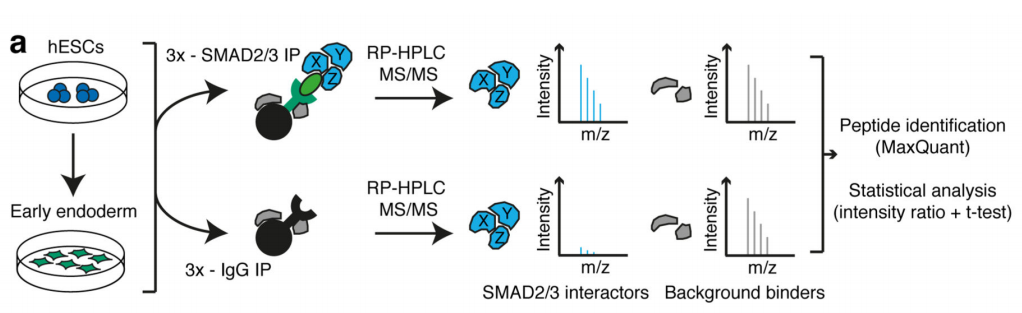

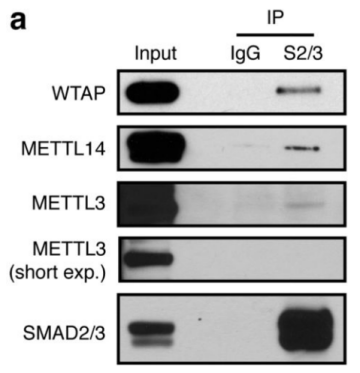
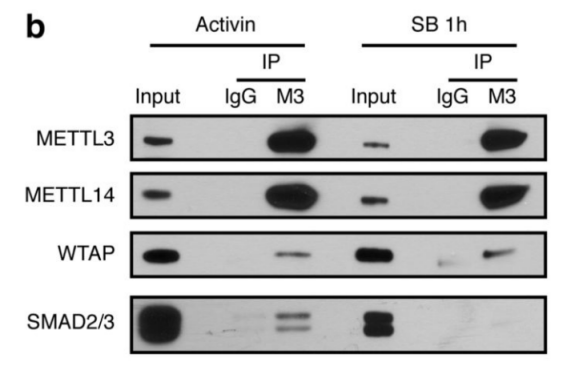
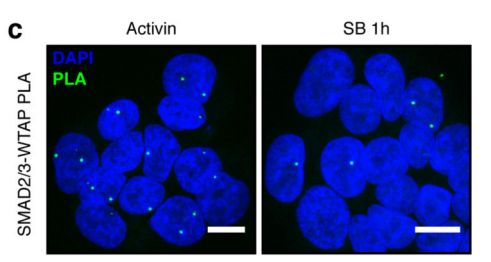
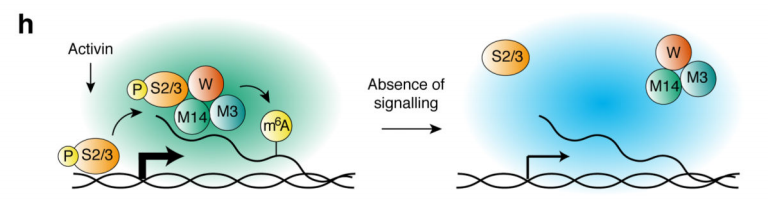
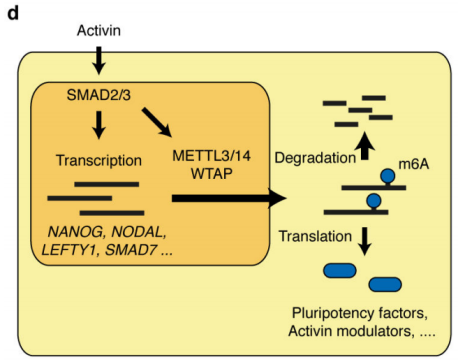
This article is the first to study the complex intracellular biological processes between the SMAD2/3 protein and the TGF-β pathway. The results demonstrate that SMAD2/3 plays a regulatory role in mRNA regulation, apoptosis, DNA repair and post-transcriptional regulation, and demonstrates that this process is regulated by methylation of activin/Nodal m6A and methylation The association between enzymes. This article lays the foundation for the study of non-canonical mechanisms of RNA methylation, such as chromatin epigenetics, transcription and epitope regulation.
Full text link
Https://
1.Yang D, Qiao J, Wang G, et al. N6-Methyladenosine modification of lincRNA 1281 is critically required for mESC differentiation potential [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46. Impact factor: 11.561
2.Wen J, Lv R, Ma H, et al. Zc3h13 Regulates Nuclear RNA m6A Methylation and Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal. [J]. Molecular Cell, 2018, 69(6):1028. Impact factor: 14.248
3.Li HB, Tong J, Zhu S, et al. m6A mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways[J]. Nature, 2017, 548(7667):338-342. Factor: 41.577?
Cloud sequence biological RNA methylation product list 
Cloud order related product recommendation
Past review
Shanghai Cloud-seq Biotech Co., Ltd.
Address: 3rd Floor, Building 20, No. 518, Zhangzhu Road, Songjiang District, Shanghai 
Telephone Fax Website:
mailbox:
SMAD2/3 and TGF-β pathway synergistically affect transcription factor m6A RNA methylation regulates stem cell development
Nature | SMAD2/3 and TGF-β pathway synergistically affect transcription factor m6A RNA methylation regulates stem cell development
Article introduction:
For more details, let's move on.
Article content:
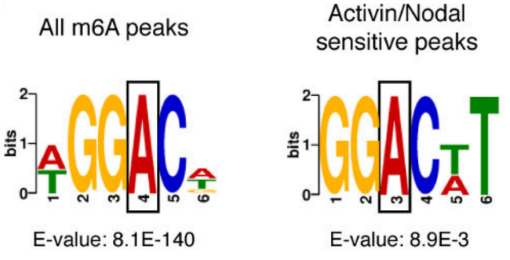
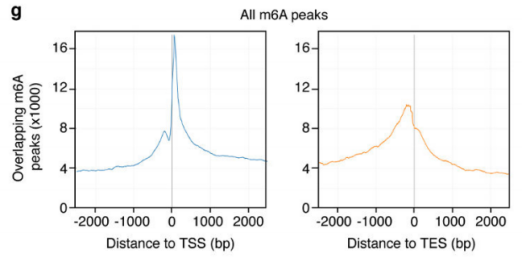
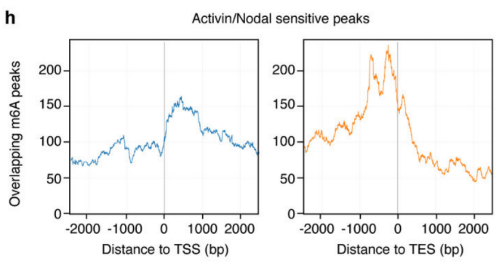
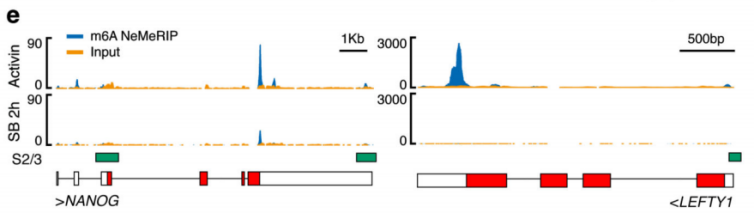
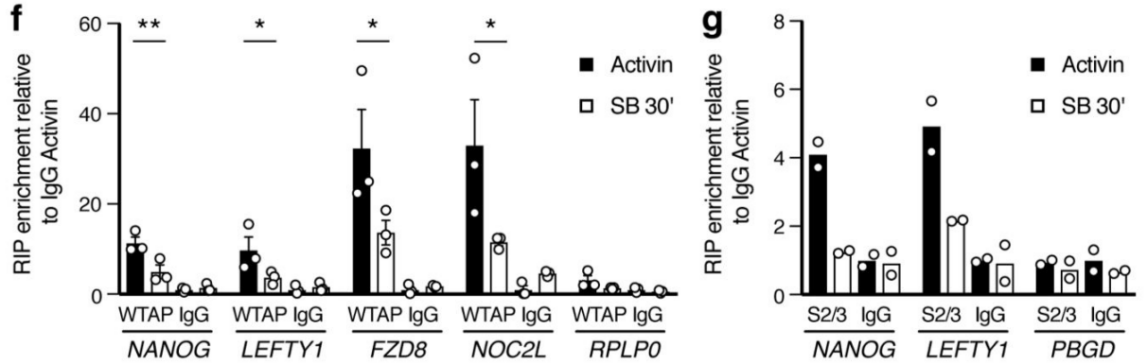
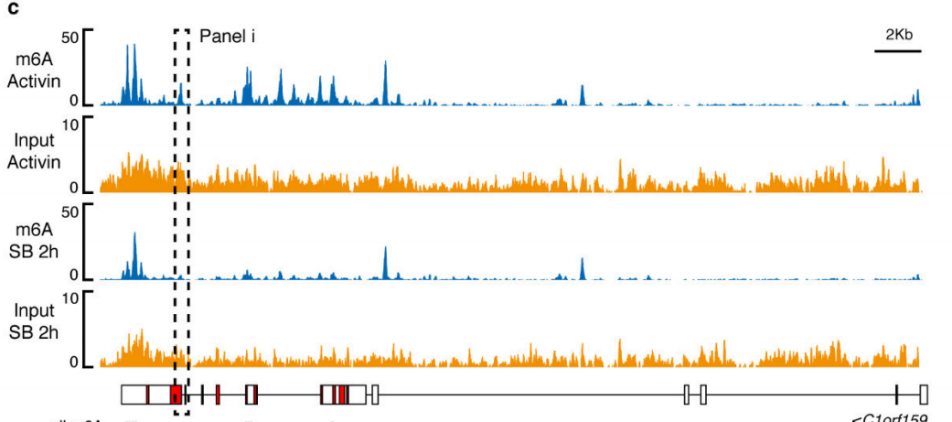
2.Activin / Nodal Effect experiment SMAD2 / 3 methylation of transcription factors to <br> of Activin / Nodal knockdown group embryonic stem cells, non-knockdown group as a control, groups of three biological repeats, for m6A RNA Methylation sequencing (Cloud Sequence Bio provides this experiment) . The results showed that the motif sequence of the motif region was GGAC, and most of them were enriched in the transcription initiation region and transcription termination region, and the Activin/Nodal specific methylation site was enriched in the transcription initiation region. Visualization results showed that the m6A methylation signal was present on the mRNA molecules of NANOG and LEFTY1 (as indicated by the red box), and a part of the region was methylated by ChIP sequencing of SMAD2/3 (the cloud sequence organism provided this experiment) . The signals overlap (as shown by the green box). The WTAP or SMAD2/3 protein RIP assay (provided by the cloud-sequence organism) demonstrated that WTAP binds to NANOG, LEFT, FZD8 and NOC2L under stimulation by Actin molecules, and promotes it under SMAD2/3 molecular stimulation. degradation.
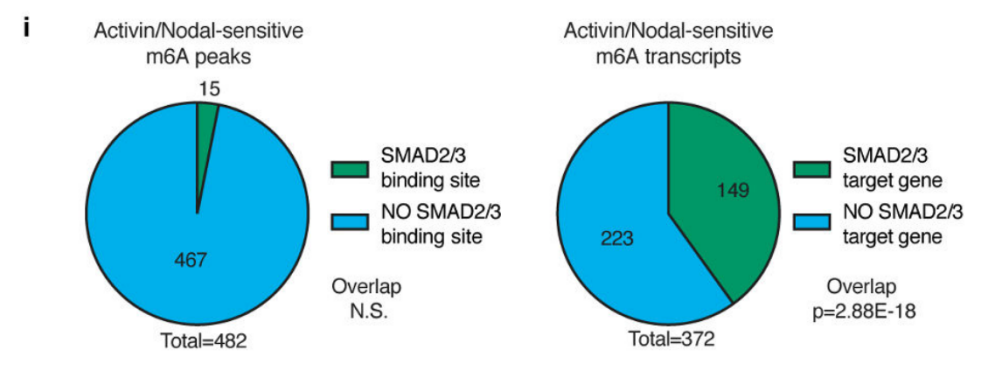
3.Activin/Nodal promotes binding of SMAD2/3 binding protein to downstream transcription factors <br> Previous studies have confirmed that m6A promotes pre-RNA synthesis in the nucleus, since SMAD2/3 in this experiment is complexed with m6A methylase The binding of the substance, which affects the synthesis of the target gene, is also in the nucleus, and the transcription and methylation of SMAD2/3 are regulated by Activin/Nodal. Therefore, the authors speculate that SMAD2/3 may be involved in the synthesis of pre-mRNA. By detecting the methylation level of m6A RNA after inhibition of Activin/Nodal, it was found that differential methylation was not only up-regulated in the exon, but also inhibited at the junction of exons and introns. In conclusion, Actin regulates the m6A RNA methylation of target genes by promoting phosphorylation of SMAD2/3 protein binding to downstream transcription factors.
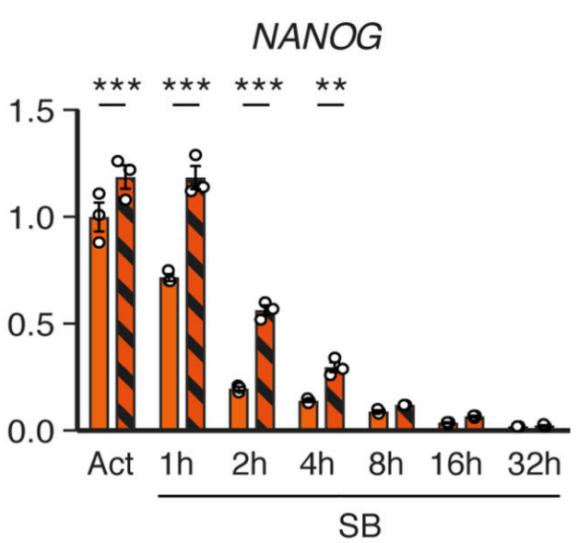
4. Transcription factor mRNA methylation negatively regulates stem cell proliferation <br> Generally speaking, RNA methylation is closely related to gene expression. The authors then analyzed a combination of methylation and transcript levels and found that the m6A methylation level on NNANOG was inversely proportional to the expression level after down-regulating the Activin/Nodal pathway, and promoted neuroectodermal differentiation.
to sum up
references
Shanghai Yunxu Biological Technology Co., Ltd.
