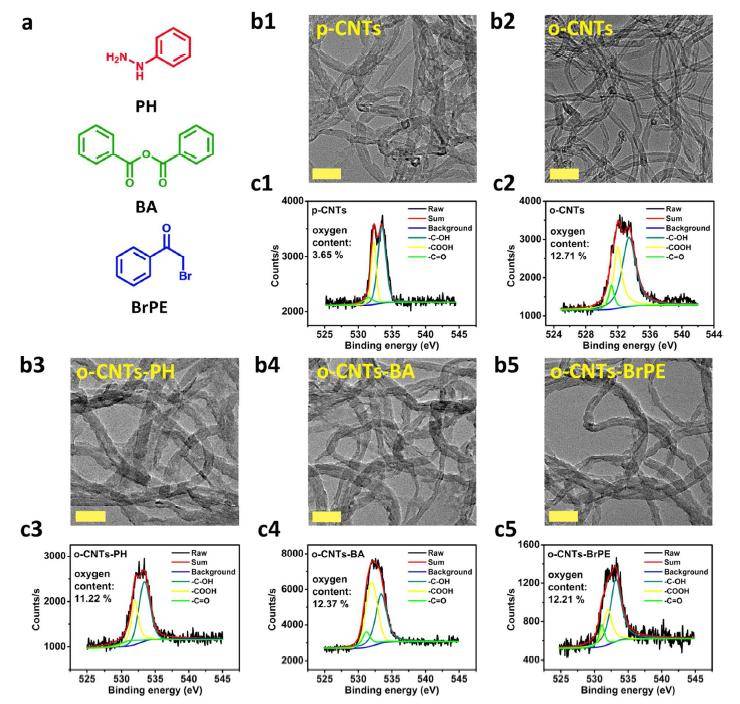
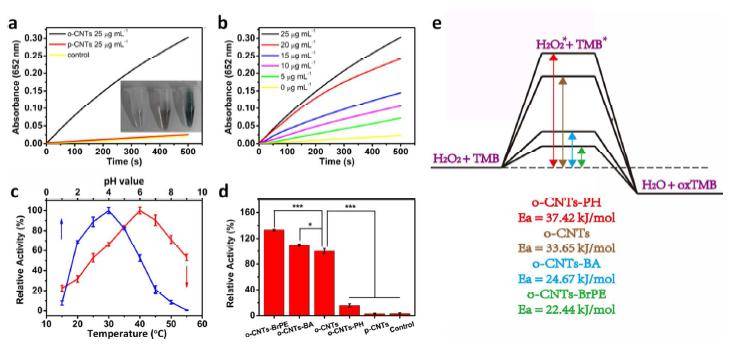
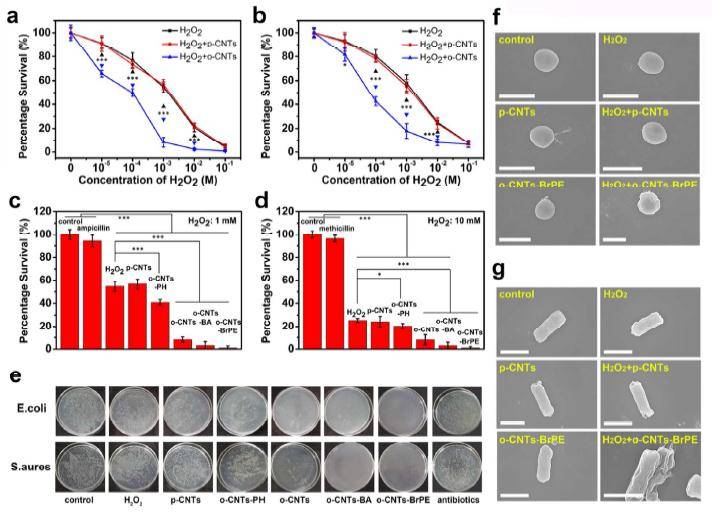
ã€introduction】 The natural enzyme has high substrate selectivity and biocatalytic performance, and has extremely high bioreactive catalytic efficiency under mild conditions. However, the low stability, high sensitivity and difficult recycling characteristics of natural enzymes hinder their practical application in various fields. In order to overcome these difficulties, the use of nanomaterials to mimic the activity of natural enzymes has become a current research hotspot. As one of the important components of non-metallic nano-enzymes, carbon nanotubes and their derivatives have received extensive attention from researchers. However, carbon nanotube-based nanozymes have low biocatalytic properties and almost no catalytic activity in a neutral environment, which largely limits their use in biomedicine. [Introduction] Recently, Qu Xiaogang team of Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, used a green method to synthesize oxidized carbon nanotubes (o-CNTs) for simulating natural peroxidase. At the same time, by combining theoretical calculations and experiments, it is proved that the enzymatic activity of oxidized carbon nanotubes is derived from the rich oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface. Among them, the carbonyl group on the surface of the oxidized carbon nanotube is the active site of the catalytic process, and the carboxyl group and the hydroxyl group are the competitive inhibition sites. Compared with the hydroxyl group, the carboxyl group has a stronger binding ability to the substrate, and thus the degree of inhibition of the catalytic reaction is stronger. This mechanism of reducing catalytic performance by competing with a catalytic site to bind a substrate is defined as "competitive inhibition." The team further chemically reduced the amount of surface carboxyl groups, thereby increasing the catalytic activity of o-CNTs. Since o-CNTs can mimic peroxidase under physiological conditions and catalyze the production of hydroxyl radicals by hydrogen peroxide, the team combines oxidized carbon nanotubes and a very small amount of hydrogen peroxide for the treatment of wound bacterial infections, avoiding the use of excessive hydrogen peroxide removal. A series of side effects caused by bacteria. [Graphic introduction] Figure 1 The catalytic mechanism of o-CNTs mimicking natural peroxidase Figure 2 Characterization of o-CNTs and their derivatives (a) Molecular structural formula of PH, BA, and BrPE (b) TEM images of p-CNTs, o-CNTs, o-CNTs-PH, o-CNTs-BA, o-CNTs-BrPE (c) p-CNTs, O1s XPS spectra of o-CNTs, o-CNTs-PH, o-CNTs-BA, o-CNTs-BrPE Figure 3 Enzymatic activity of o-CNTs (a) o-CNTs, peroxidase activity of p-CNTs (b) peroxidase activity of different concentrations of o-CNTs (c) effect of different temperature/pH on enzymatic activity of o-CNTs (d)o Comparison of enzymatic activities of -CNTs and their derivatives (e) Schematic diagram of enzymatic reaction activation energy of o-CNTs and their derivatives Figure 4 Antibacterial effect of o-CNTs and their derivatives Figure 5 live experiment (a) Schematic diagram of treatment of wound infection based on o-CNTs nanozymes (b) Treatment effect at different time points (c) Changes in wound area over time (d) Effect of different treatment regimens on bacterial growth at wound tissue Cloth plate method) Figure 6 Pathological analysis of the wound (a) Histological analysis of wound healing processes (b) Immunohistochemical analysis of skin tissue healing processes (c) Quantitative evaluation of collagen formation (d) Quantitative evaluation of angiogenesis ã€summary】 O-CNTs with high peroxidase activity were synthesized using a green synthetic method, and the mechanism of enzyme activity was explained in combination with theoretical calculations and experiments. At the same time, the use of nanozymes for the treatment of wound bacterial infections avoids a series of side effects caused by the use of excess hydrogen peroxide to remove bacteria. Dried Fruit,Freeze Dried Strawberries,Dehydrated Fruit,Dried Goji Berries Xi'an Gawen Biotechnology Co., Ltd , https://www.seoagolyn.com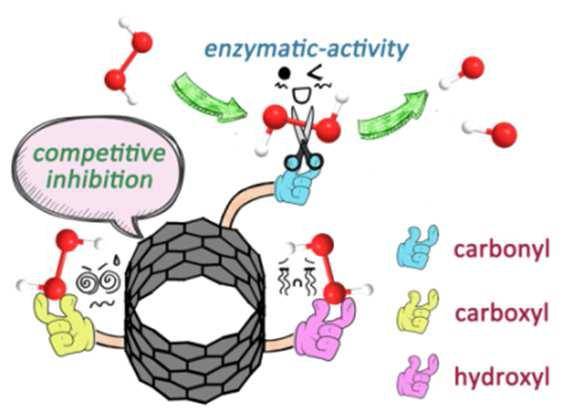
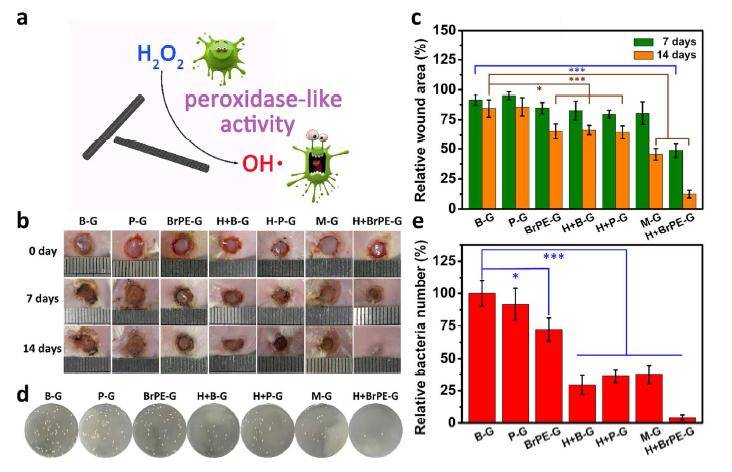
(e) Effects of different treatment regimens on the number of bacteria in wound tissue (quantitative statistics) 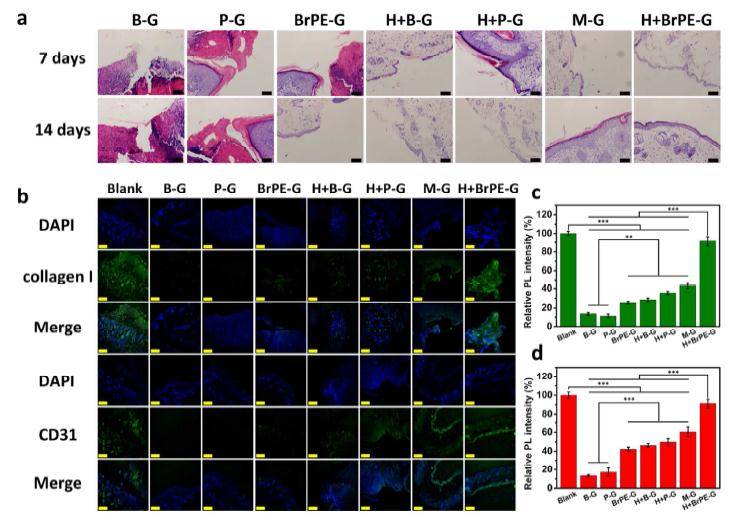
Enzyme activity of oxygenated carbon nanotubes in the treatment of bacterial infections
