About a month after the grape leaves fall to about a month and a half before germination in the spring of the following year, it is usually the ideal period for grape pruning. In cold-proof areas with buried soil, the initial shear is generally completed before burial. Before and after the grape leaves fall, the nutrients in the branches and leaves are transferred to the old vines and root storage. After the winter, the weather becomes warmer, and the nutrients stored in the old vines and roots begin to transport to the branches and leaves. According to these characteristics of grape growth and development, pruning too early or pruning too late will cause the loss of nutrients. In addition, pruning too early will also reduce the cold resistance of the vine, and pruning too late will easily weaken the tree vigor. Basic techniques and pruning Short-cutting Short-cutting is a pruning method that cuts off a part of the branches that were born in the year. The retained length of the branches determines the weight of the short cut. Through the short cut, the nutrients accumulated in the tree body and root system in the previous year are concentrated in the eyes of the remaining buds, so as to better promote the growth and development of the buds in the coming year. Thinning Thinning is a method of completely removing the entire branch from the base. Thinning can remove dense branches and poorly-grown branches, improve field lighting conditions and nutrient distribution, and leave well-developed and robust branches, so that plants can grow in a balanced manner, thereby achieving the goal of high quality and high yield. Shrinkage is a pruning method that cuts off branches that are two years old or more than two years old. By shrinking, old branches can be rejuvenated or the growth direction can be changed. Pruning method and applicable varieties Very short shoot pruning is called extremely short shoot pruning when only one bud is retained after pruning the branches. Very short shoot pruning is suitable for varieties with good fruiting traits, orchards with good flower bud differentiation and frame styles. Generally, European and American hybrids such as Jingya, Kyoho, etc., have a low flower bud differentiation node. If the management is standard, and when the flower bud differentiation is generally good when using a trellis or a horizontal frame, consider very short shoot pruning. Short shoot pruning is called short shoot pruning when only 2 to 3 buds remain after the pruning of the shoots. Varieties suitable for short shoot pruning include European and American hybrids such as Jingya and Kyoho, as well as other varieties with better fruiting traits such as Victoria and Crimson. Short shoot pruning can be used in plots with relatively standardized management and better flower bud differentiation. Mid-tip pruning is called mid-tip pruning, which retains 4 to 7 buds after pruning the original branches. It is suitable for Eurasian species with medium growth vigor, high fruiting branch rate and low flower bud implantation position, such as Victoria, red earth, ruby ​​seedless, etc. The pruning of long shoots and extra-long shoots that retain 8 to 11 buds after pruning the branches of the year is called long shoot pruning. Long shoot pruning is suitable for Eurasian species with vigorous growth, low fruiting shoot rate, and high flower bud implantation positions, such as Meirenzhi and Crimson Seedless. After pruning the shoots that year, more than 12 buds are retained, which is called ultra-long shoot pruning. The pruning of the extension heads of most varieties mostly adopts super long tip pruning. Determine the length of the result Grape varieties with different variety characteristics have obvious differences in their fruiting habits. The result habit is an important basis for the cutting length of the result mother branch, and the cutting length should refer to this habit. Generally speaking, varieties with strong knot strength are suitable for pruning short shoots and medium and short shoots, such as Kyoho, Hutai 8 and other European and American hybrid varieties; varieties with vigorous growth and low seed setting rate are suitable for pruning methods with long shoots and medium shoots. , Such as Eurasian species, Oriental species group species Meirenzhi, Crimson Seedless, etc.; Red Earth species are suitable for mixed pruning of long, medium and short shoots. Environmental conditions The growth of grapes is different, and the growth and development of its branches are also very different. In dry and rainless areas, the flower buds differentiate well. For the same species, the fruiting position is generally lower than that in other areas. Therefore, the pruning should be appropriately reduced compared to other areas. In the rainy areas of our country, the cut-off node position should be adapted to increase. In sandy soil conditions, due to the large temperature difference between day and night, the flower bud differentiation is relatively good, and the number of cutting nodes should be appropriately reduced. Cultivation and management Cultivation conditions are also an important basis for the length of grape fruiting branches. In summer, when the management is standardized, the new shoots are topped many times, and the prevention and control of downy mildew in the later period is timely and does not cause a major impact, the grape flower bud differentiation will be better. When pruning in winter, the cutting length can be shortened appropriately. In the case of excessive nitrogen application and excessive growth of new shoots, when pruning in winter, the cutting length of branches needs to be extended appropriately. The growth status of branches The growth angle of annual branches determines the quality of flower bud differentiation. Generally speaking, the current-year-old branches on the trellis and horizontal shelves grow relatively flat, and the flower buds are generally well differentiated. The branches left during pruning can be shorter; while the upright branches have relatively poor flower bud differentiation and can be cut appropriately. For a branch, the quality of the base bud eye is poor, the quality of the middle and upper bud eye is better, and the seed setting rate is higher. According to this characteristic, people are accustomed to keeping the tips longer to increase the yield, but an obvious disadvantage of this method is that the results will move up year by year, so use short, medium, and long tips to prun the mix, and pay attention to the results. The relationship with the update, to avoid the result part moving up too much. Generally speaking, for weakly growing branches, the cut should be shorter. As a result, the thickness of the branches is also an important basis for affecting the cutting length. When the new shoot is very thick (diameter above 1.2 cm), the length of the cut should be increased appropriately, and the part with the diameter below 1.2 cm should be retained, and the shoots with appropriate thickness should be used to produce new shoots. Disclaimer: Some articles on this website are transferred from the Internet. If the legal rights of a third party are involved, please inform this website for processing. phone
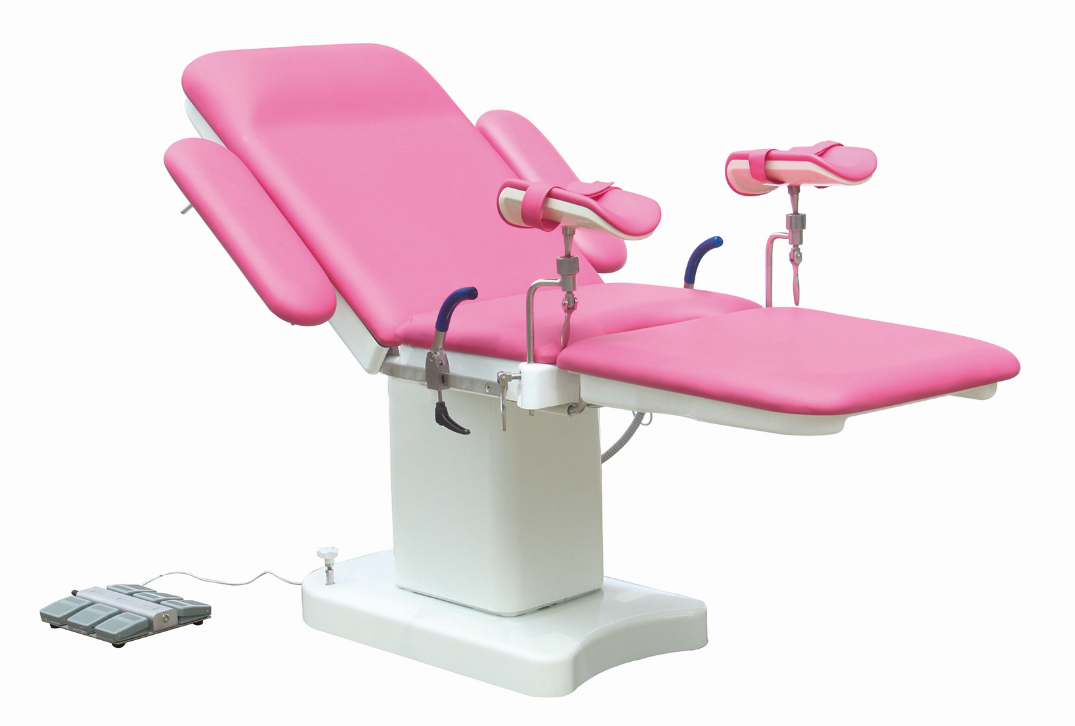
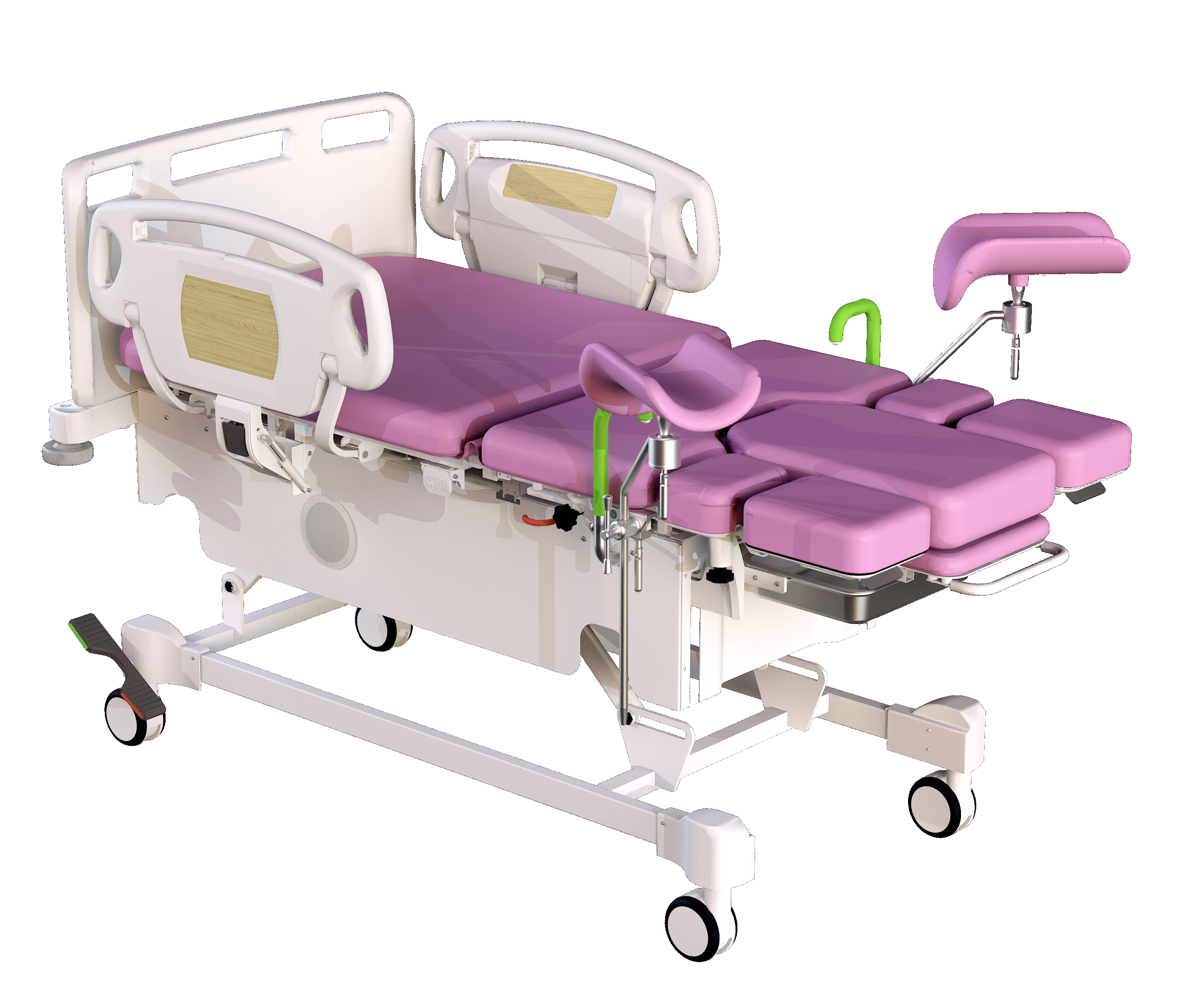
Multifunctional Obstetric Examination Bed
is for the modern hospital elaborates designed with childbirth, gynecologic
operation, diagnosis and examination, including emergency caesarean section in
a variety of medical functional bed. Obstetric Table table selection of high quality polyurethane foam, leather
bags, easy cleaning and disinfection. We have R&D center in Shandong, Shanghai, Shenzhen to launch new products to meet the needs for hospital every year. We have more than 50,000 square meters workshop and R&D building, which is characterized by high quality products and advanced technology.
Obstetric Table,Gynecologic Table,Woman Delivery Table,Gynecological Table Shandong Lewin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.lewinmed.com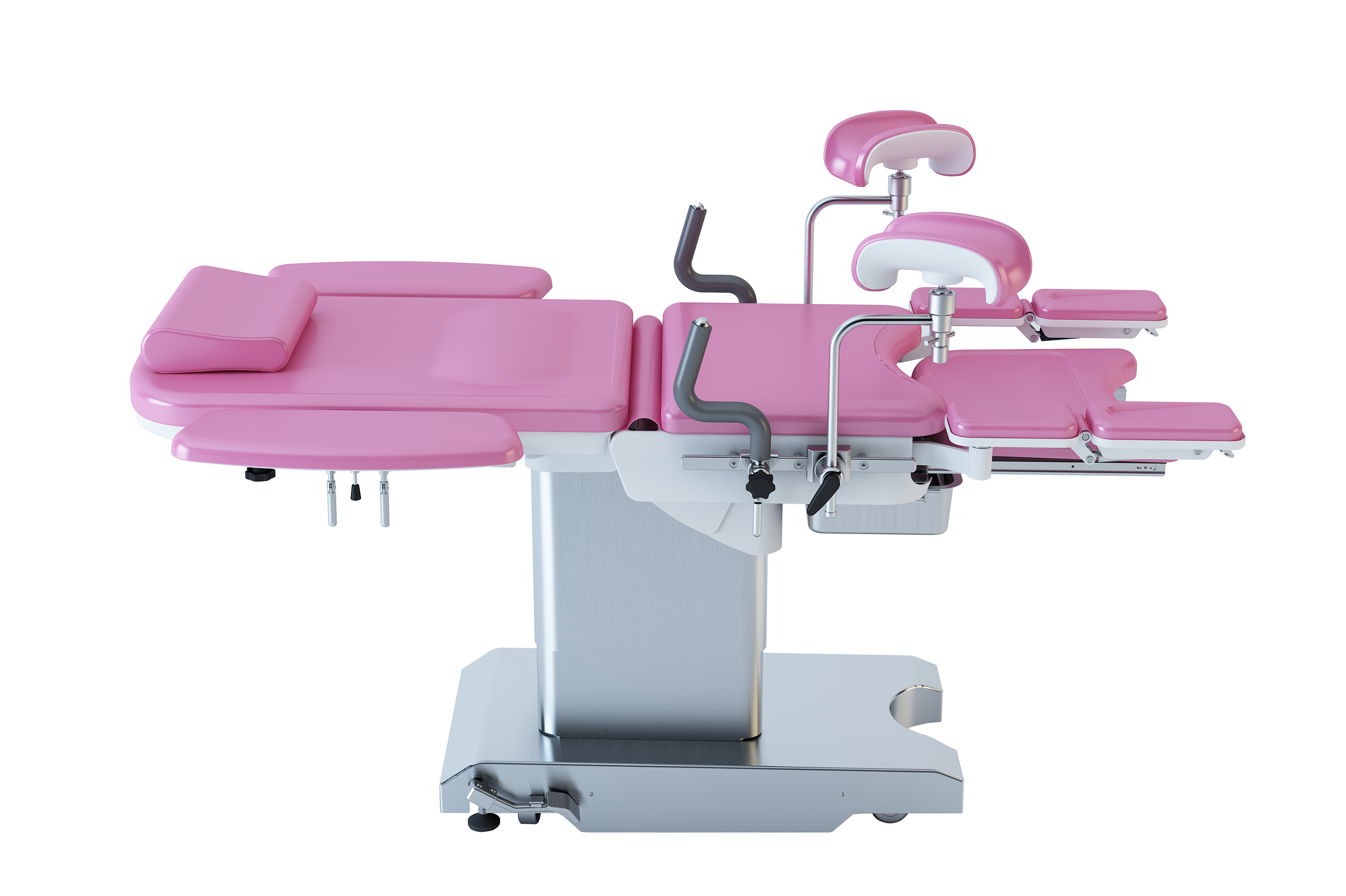
There are techniques for grape winter cutting, these points must be kept in mind
